Functional dissection of in vivo interchromosome association in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 11056536
- PMCID: PMC2673479
- DOI: 10.1038/35041055
Functional dissection of in vivo interchromosome association in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
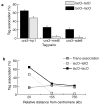
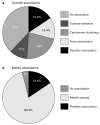
Homologue pairing mediates both recombination and segregation of chromosomes at meiosis I. The recognition of nucleic-acid-sequence homology within the somatic nucleus has an impact on DNA repair and epigenetic control of gene expression. Here we investigate interchromosomal interactions using a non-invasive technique that allows tagging and visualization of DNA sequences in vegetative and meiotic live yeast cells. In non-meiotic cells, chromosomes are ordered in the nucleus, but preferential pairing between homologues is not observed. Association of tagged chromosomal domains occurs irrespective of their genomic location, with some preference for similar chromosomal positions. Here we describe a new phenomenon that promotes associations between sequence-identical ectopic tags with a tandem-repeat structure. These associations, termed interchromosome trans-associations, may underlie epigenetic phenomena.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

