Human DNA polymerase kappa synthesizes DNA with extraordinarily low fidelity
- PMID: 11058111
- PMCID: PMC113146
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/28.21.4147
Human DNA polymerase kappa synthesizes DNA with extraordinarily low fidelity
Abstract
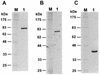
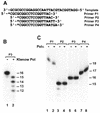
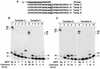
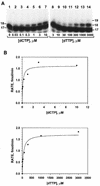
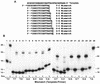
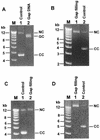
Escherichia coli DNA polymerase IV encoded by the dinB gene is involved in untargeted mutagenesis. Its human homologue is DNA polymerase kappa (Polkappa) encoded by the DINB1 gene. Our recent studies have indicated that human Polkappa is capable of both error-free and error-prone translesion DNA synthesis in vitro. However, it is not known whether human Polkappa also plays a role in untargeted mutagenesis. To examine this possibility, we have measured the fidelity of human Polkappa during DNA synthesis from undamaged templates. Using kinetic measurements of nucleotide incorporations and a fidelity assay with gapped M13mp2 DNA, we show that human Polkappa synthesizes DNA with extraordinarily low fidelity. At the lacZalpha target gene, human Polkappa made on average one error for every 200 nucleotides synthesized, with a predominant T-->G transversion mutation at a rate of 1/147. The overall error rate of human Polkappa is 1.7-fold lower than human Poleta, but 33-fold higher than human Polbeta, a DNA polymerase with very low fidelity. Thus, human Polkappa is one of the most inaccurate DNA polymerases known. These results support a role for human Polkappa in untargeted mutagenesis surrounding a DNA lesion and in DNA regions without damage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Error-free and error-prone lesion bypass by human DNA polymerase kappa in vitro.Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Nov 1;28(21):4138-46. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.21.4138. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000. PMID: 11058110 Free PMC article.
-
Error-prone and inefficient replication across 8-hydroxyguanine (8-oxoguanine) in human and mouse ras gene fragments by DNA polymerase kappa.Genes Cells. 2005 Jun;10(6):543-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2005.00858.x. Genes Cells. 2005. PMID: 15938713
-
Quantitative analysis of translesion DNA synthesis across a benzo[a]pyrene-guanine adduct in mammalian cells: the role of DNA polymerase kappa.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 17;279(51):53298-305. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409155200. Epub 2004 Oct 9. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15475561
-
Structure of human DNA polymerase iota and the mechanism of DNA synthesis.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012 Jun;77(6):547-61. doi: 10.1134/S0006297912060016. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2012. PMID: 22817454 Review.
-
Translesion synthesis by the UmuC family of DNA polymerases.Mutat Res. 2001 Jul 12;486(2):59-70. doi: 10.1016/s0921-8777(01)00089-1. Mutat Res. 2001. PMID: 11425512 Review.
Cited by
-
Cyclin Kinase-independent role of p21CDKN1A in the promotion of nascent DNA elongation in unstressed cells.Elife. 2016 Oct 14;5:e18020. doi: 10.7554/eLife.18020. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27740454 Free PMC article.
-
A Role for N6-Methyladenine in DNA Damage Repair.Trends Biochem Sci. 2021 Mar;46(3):175-183. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.09.007. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Trends Biochem Sci. 2021. PMID: 33077363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An underlying mechanism for the increased mutagenesis of lagging-strand genes in Bacillus subtilis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Mar 10;112(10):E1096-105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1416651112. Epub 2015 Feb 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25713353 Free PMC article.
-
The absence of Mth1 inactivation and DNA polymerase kappa overexpression in rat mammary carcinomas with frequent A:T to C:G transversions.Jpn J Cancer Res. 2002 May;93(5):501-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2002.tb01284.x. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12036445 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of specialized DNA polymerases expression in human gliomas: association with prognostic significance.Neuro Oncol. 2010 Jul;12(7):679-86. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nop074. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Neuro Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20164241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goodman M.F. (2000) Trends Biochem. Sci., 25, 189–195. - PubMed
-
- Goodman M.F. and Tippin,B. (2000) Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 10, 162–168. - PubMed
-
- Tang M., Pham,P., Shen,X., Taylor,J.S., O’Donnell,M., Woodgate,R. and Goodman,M.F. (2000) Nature, 404, 1014–1018. - PubMed
-
- Reuven N.B., Arad,G., Maor-Shoshani,A. and Livneh,Z. (1999) J. Biol. Chem., 274, 31763–31766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

