The thy pol-2 intein of Thermococcus hydrothermalis is an isoschizomer of PI-TliI and PI-TfuII endonucleases
- PMID: 11058140
- PMCID: PMC113141
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/28.21.4391
The thy pol-2 intein of Thermococcus hydrothermalis is an isoschizomer of PI-TliI and PI-TfuII endonucleases
Abstract
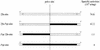
THY Pol-2 intein, from Thermococcus hydrothermalis, belongs to the same allelic family as TLI Pol-2 (PI-TLII), Tfu Pol-2 (PI-TFUII) and TspTY Pol-3 mini-intein, all inserted at the pol-c site of archaeal DNA polymerase genes. This new intein was cloned, expressed in Escherichia coli and purified. The intein is a specific endonuclease (PI-THY:I) which cleaves the inteinless sequence of the THY DNA pol gene. Moreover, PI-TLII, PI-TFUII and PI-THYI are very similar endonucleases which cleave DNA in the same optimal conditions at 70 degrees C yielding similar 3'-hydroxyl overhangs of 4 bp and the reaction is subject to product inhibition. The three enzymes are able to cleave the three DNA sequences spanning the pol-c site and a 24 bp consensus cleavage site was defined for the three isoschizomers. However, the exact size of the minimal cleavage site depends both on the substrate sequence and the endonuclease. The inability of the isoschizomers to cleave the inteinless DNA polymerase gene from Pyrococcus spp. KOD is due to point substitutions on the 5' side of the pol-c site, suggesting that the absence of inteins of this allelic family in DNA polymerase genes from Pyrococcus spp. can be linked to small differences in the target site sequence.
Figures





References
-
- Hirata R., Ohsumi,Y., Nakano,A., Kawasaki,H., Suzuki,K. and Anraku,Y. (1990) J. Biol. Chem., 265, 6726–6733. - PubMed
-
- Kane P.M., Yamashiro,C.T., Wolczyk,D.F., Neff,N., Goebl,M. and Stevens,T.H. (1990) Science, 250, 651–657. - PubMed
-
- Inteins-protein introns web site at http://www.blocks.fhcrc.org/∼pietro/inteins/
-
- Inbase, the New England Biolabs intein database at http://www.neb.com/neb/inteins/ - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

