Sensory deprivation without competition yields modest alterations of short-term synaptic dynamics
- PMID: 11058162
- PMCID: PMC18855
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.230175697
Sensory deprivation without competition yields modest alterations of short-term synaptic dynamics
Abstract
Cortical maps express experience-dependent plasticity. However, the underlying cellular mechanisms remain unclear. We have recently shown that sensory deprivation results in large changes of the short-term dynamics of excitatory synapses at the junction of deprived and spared somatosensory (barrel) cortex, which may contribute to map reorganization. A key issue is whether the alterations in short-term synaptic dynamics are driven by a loss of sensory input or by competition between deprived and spared inputs. Here, we report that short-term dynamics of horizontal pathways in the middle of uniformly deprived cortex change only modestly. Vertical intracortical pathways were unaffected by deprivation. Our results suggest that uniform loss of sensory activity has a limited effect on short-term synaptic dynamics. We concluded that competition between sensory inputs is necessary to produce large-scale changes in synaptic dynamics after sensory deprivation.
Figures
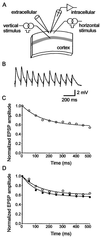
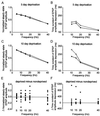
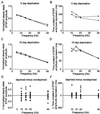
Similar articles
-
Sensory experience modifies the short-term dynamics of neocortical synapses.Nature. 1999 Jul 22;400(6742):367-71. doi: 10.1038/22553. Nature. 1999. PMID: 10432115
-
Long-term depression induced by sensory deprivation during cortical map plasticity in vivo.Nat Neurosci. 2003 Mar;6(3):291-9. doi: 10.1038/nn1012. Nat Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12577061
-
Vision loss shifts the balance of feedforward and intracortical circuits in opposite directions in mouse primary auditory and visual cortices.J Neurosci. 2015 Jun 10;35(23):8790-801. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4975-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26063913 Free PMC article.
-
Reconciling homeostatic and use-dependent plasticity in the context of somatosensory deprivation.Neural Plast. 2015;2015:290819. doi: 10.1155/2015/290819. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Neural Plast. 2015. PMID: 25866682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-modal synaptic plasticity in adult primary sensory cortices.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2015 Dec;35:119-26. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2015.08.002. Epub 2015 Aug 25. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 26310109 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A metaplasticity view of the interaction between homeostatic and Hebbian plasticity.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Mar 5;372(1715):20160155. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0155. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28093549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensory deprivation during early development causes an increased exploratory behavior in a whisker-dependent decision task.Brain Behav. 2013 Jan;3(1):24-34. doi: 10.1002/brb3.102. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Brain Behav. 2013. PMID: 23408764 Free PMC article.
-
A model of order-selectivity based on dynamic changes in the balance of excitation and inhibition produced by short-term synaptic plasticity.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Jan 15;113(2):509-23. doi: 10.1152/jn.00568.2014. Epub 2014 Oct 22. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25339707 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental shift of short-term synaptic plasticity in cortical organotypic slices.Neuroscience. 2012 Jun 28;213:38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.04.018. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22521823 Free PMC article.
-
Information transfer and recovery for the sense of touch.Cereb Cortex. 2025 Apr 1;35(4):bhaf073. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhaf073. Cereb Cortex. 2025. PMID: 40197640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Merzenich M M, Kaas J H, Wall J, Nelson R J, Sur M, Felleman D. Neuroscience. 1983;8:33–55. - PubMed
-
- Kaas J H, Krubitzer L A, Chino Y M, Langston A L, Polley E H, Blair N. Science. 1990;248:229–231. - PubMed
-
- Robertson D, Irvine D. J Comp Neurol. 1989;282:456–471. - PubMed
-
- Wiesel T N, Hubel D H. J Neurophysiol. 1963;26:1003–1017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

