Detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in klebsiellae with the Oxoid combination disk method
- PMID: 11060096
- PMCID: PMC87569
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.11.4228-4232.2000
Detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in klebsiellae with the Oxoid combination disk method
Abstract
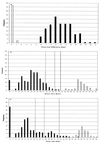
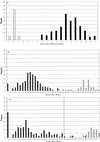
The Oxoid combination disk method for detecting extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs) depends on comparing the inhibition zones of cefpodoxime (10-microg) and cefpodoxime-plus-clavulanate (10- plus 1-microg) disks. The presence of clavulanate enlarged the zones for all of 180 ESBL-producing klebsiellae by >/=5 mm, whereas zones for cefpodoxime-susceptible isolates and cefpodoxime-resistant isolates with AmpC and K1 beta-lactamases were enlarged by </=1 mm. Good discrimination was achieved with either the NCCLS or the British disk method.
Figures
References
-
- Babini G S, Livermore D M. Antimicrobial resistance amongst Klebsiella spp. collected from intensive care units in Southern and Western Europe in 1997–1998. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000;45:183–189. - PubMed
-
- Brun-Buisson C, Legrand P, Philippon A, Montravers F, Ansquer M, Duval J. Transferable enzymatic resistance to third-generation cephalosporins during nosocomial outbreak of multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Lancet. 1987;ii:302–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

