Sources on the anterior and posterior banks of the central sulcus identified from magnetic somatosensory evoked responses using multistart spatio-temporal localization
- PMID: 11061334
- PMCID: PMC6872012
- DOI: 10.1002/1097-0193(200010)11:2<59::aid-hbm10>3.0.co;2-5
Sources on the anterior and posterior banks of the central sulcus identified from magnetic somatosensory evoked responses using multistart spatio-temporal localization
Abstract
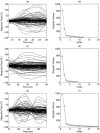
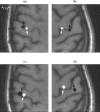
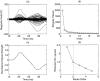
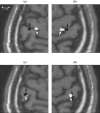
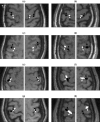
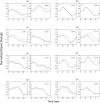
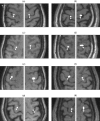
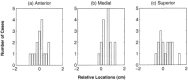
A Multi-Start Spatio-Temporal (MSST) multidipole localization algorithm was used to study sources on the anterior and posterior banks of the central sulcus localized from early somatosensory magnetoencephalography (MEG) responses. Electrical stimulation was applied to the right and left median nerves of 8 normal subjects. Two sources, one on the anterior and one on the posterior bank of the central sulcus, were localized from 16 data sets (8 subjects, 2 hemispheres). Compared with the more traditional practice of single-dipole fits to peak latencies, MSST provided more reliable source locations. The temporal dynamics of the anterior and posterior central sulcus sources, obtained using MSST, showed considerable temporal overlap. In some cases, the two sources appeared synchronous. On the other hand, in the traditional single-dipole peak-latency fit approach, there is no time course other than a focal dipole moment activated only at the selected peak latency. The same group of subjects also performed a motor task involving index-finger lifting; the anterior central sulcus source obtained from electrical median nerve stimulation localized to the same or similar region in the primary motor area identified from the finger-lift task. The physiological significance of the anterior central sulcus source is discussed. The findings suggest that one can test the integrity of cortical tissue in the region of primary motor cortex using electrical somatosensory stimulation.
Figures
References
-
- Achim A, Richer F, Saint‐Hilaire JM. (1991): Methodological consideration for the evaluation of spatio‐temporal source models. Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol 79: 227–240. - PubMed
-
- Aine C, Huang M, Stephen J, Christner R. (2000): Multi‐start algorithms for MEG empirical data analysis reliably characterize locations and time‐courses of multiple sources. NeuroImage 12: 159–172. - PubMed
-
- Allison T, Wood CC, McCarthy G, Spencer DD. (1991a): Cortical somatosensory evoked potentials. II. Effects of excision of somatosensory or motor cortex in humans and monkeys. J Neurophysiol 66: 64–82. - PubMed
-
- Allison T, McCarthy G, Wood CC, Jones SJ. (1991b): Potentials evoked in human and monkey cerebral cortex by stimulation of the median nerve. Brain 114: 2465–2503. - PubMed
-
- Ahonen AI, Hämäläinen MS, Kajola MJ, Knuutila JET, Laine. (1992): A 122‐channel magnetometer covering the whole head. In: Dittmar A, Froment JC, eds): Proceedings of the Satellite Symposium on Neuroscience and Technology, 14th annual conference of IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society: IEEE Engineering and Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 16–20.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

