Quantitative maps of GAbAergic and glutamatergic neuronal systems in the human brain
- PMID: 11061336
- PMCID: PMC6872118
- DOI: 10.1002/1097-0193(200010)11:2<93::AID-HBM30>3.0.CO;2-Y
Quantitative maps of GAbAergic and glutamatergic neuronal systems in the human brain
Abstract
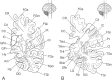
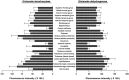
GABAergic and glutamatergic neuronal systems in adult normal human brains were shown quantitatively and in detail through the distributions of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), respectively. Consecutive coronal sections containing part of the striatum and the substantia nigra were obtained from the right hemisphere of three deceased persons with no history of neurological or psychiatric diseases and were stained immunohistochemically for GAD and GDH. Each stained section was divided into approximately 3 million microareas and the immunohistochemical fluorescence intensity in each area was measured by a human brain mapping analyzer, which is a microphotometry system for analysis of the distribution of neurochemicals in a large tissue slice. In the analyzed brain regions, conspicuously intense GAD-like immunoreactivity was observed in the substantia nigra, globus pallidus, and hypothalamus. GDH was widely and rather evenly distributed in the gray matter compared to GAD, although intense GDH-like immunoreactivity was observed in the lateral geniculate nucleus and substantia nigra. Within the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, and other regions, characteristic distributions of GAD- and GDH-like immunoreactivity were found. We believe that the analysis of the human brain by this novel technique can help to understand the functional distribution of neuronal systems in the normal human brain and may be able to identify abnormal changes in the diseased human brain. It can also provide basic data to help in the interpretation of functional magnetic resonance imaging or positron emission tomography.
Figures



References
-
- Albin RL, Young AB, Penney JB (1989): The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci 12: 366–375. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, Crutcher M (1990): Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neuronal substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci 13: 266–271. - PubMed
-
- Binder GA, Haughton VM, Ho KC (1979): Computed tomography of the brain in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes. Boston: Little, Brown.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

