Epidermal growth factor and membrane trafficking. EGF receptor activation of endocytosis requires Rab5a
- PMID: 11062256
- PMCID: PMC2185585
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.3.539
Epidermal growth factor and membrane trafficking. EGF receptor activation of endocytosis requires Rab5a
Abstract
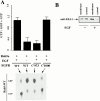
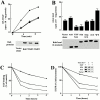
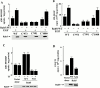
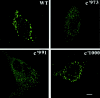
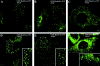
Activated epidermal growth factor receptors recruit various intracellular proteins leading to signal generation and endocytic trafficking. Although activated receptors are rapidly internalized into the endocytic compartment and subsequently degraded in lysosomes, the linkage between signaling and endocytosis is not well understood. Here we show that EGF stimulation of NR6 cells induces a specific, rapid and transient activation of Rab5a. EGF also enhanced translocation of the Rab5 effector, early endosomal autoantigen 1 (EEA1), from cytosol to membrane. The activation of endocytosis, fluid phase and receptor mediated, by EGF was enhanced by Rab5a expression, but not by Rab5b, Rab5c, or Rab5a truncated at the NH(2) and/or COOH terminus. Dominant negative Rab5a (Rab5:N34) blocked EGF-stimulated receptor-mediated and fluid-phase endocytosis. EGF activation of Rab5a function was dependent on tyrosine residues in the COOH-terminal domain of the EGF receptor (EGFR). Removal of the entire COOH terminus by truncation (c'973 and c'991) abrogated ligand-induced Rab5a activation of endocytosis. A "kinase-dead" EGFR failed to stimulate Rab5a function. However, another EGF receptor mutant (c'1000), with the kinase domain intact and a single autophosphorylation site effectively signaled Rab5 activation. These results indicate that EGFR and Rab5a are linked via a cascade that results in the activation of Rab5a and that appears essential for internalization. The results point to an interdependent relationship between receptor activation, signal generation and endocytosis.
Figures

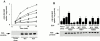

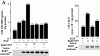
References
-
- Alvarez-Dominguez C., Stahl P.D. Interferon-gamma selectively induces Rab5a synthesis and processing in mononuclear cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:33901–33904. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Dominguez C., Stahl P.D. Increased expression of Rab5a correlates directly with accelerated maturation of Listeria monocytogenes phagosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:11459–11462. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri M.A., Hoffenberg S., Roberts R., Mukhopadhyay A., Pomrehn A., Dickey B.F., Stahl P.D. Evidence for a symmetrical requirement for Rab5:GTP in in vitro endosome–endosome fusion J. Biol. Chem 273 1998. 25850 25855a - PubMed
-
- Barbieri M.A., Kohn A.D., Roth R.A., Stahl P.D. Protein kinase B/akt and rab5 mediate Ras activation of endocytosis J. Biol. Chem 273 1998. 19367 19370b - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

