A selective transport route from Golgi to late endosomes that requires the yeast GGA proteins
- PMID: 11062260
- PMCID: PMC2185592
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.3.587
A selective transport route from Golgi to late endosomes that requires the yeast GGA proteins
Abstract
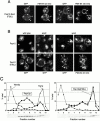
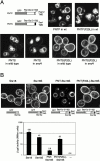
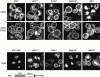
Pep12p is a yeast syntaxin located primarily in late endosomes. Using mutagenesis of a green fluorescent protein chimera we have identified a sorting signal FSDSPEF, which is required for transport of Pep12p from the exocytic pathway to late endosomes, from which it can, when overexpressed, reach the vacuole. When this signal is mutated, Pep12p instead passes to early endosomes, a step that is determined by its transmembrane domain. Surprisingly, Pep12p is then specifically retained in early endosomes and does not go on to late endosomes. By testing appropriate chimeras in mutant strains, we found that FSDSPEF-dependent sorting was abolished in strains lacking Gga1p and Gga2p, Golgi-associated coat proteins with homology to gamma adaptin. In the gga1 gga2 double mutant endogenous Pep12p cofractionated with the early endosome marker Tlg1p, and recycling of Snc1p through early endosomes was defective. Pep12p sorting was also defective in cells lacking the clathrin heavy or light chain. We suggest that specific and direct delivery of proteins to early and late endosomes is required to maintain the functional heterogeneity of the endocytic pathway and that the GGA proteins, probably in association with clathrin, help create vesicles destined for late endosomes.
Figures







References
-
- Ausubel, F.M., R. Brent, R.E. Kingston, D.D. Moore, J.G. Seidman, J.A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1995. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Vol. 1. J. Wiley and Sons, Inc., Boston, MA. 13.6.2–13.6.3.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

