Chlamydomonas IFT88 and its mouse homologue, polycystic kidney disease gene tg737, are required for assembly of cilia and flagella
- PMID: 11062270
- PMCID: PMC2185580
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.151.3.709
Chlamydomonas IFT88 and its mouse homologue, polycystic kidney disease gene tg737, are required for assembly of cilia and flagella
Abstract
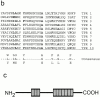
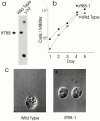
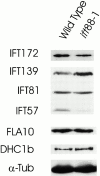
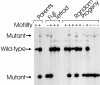
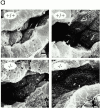
Intraflagellar transport (IFT) is a rapid movement of multi-subunit protein particles along flagellar microtubules and is required for assembly and maintenance of eukaryotic flagella. We cloned and sequenced a Chlamydomonas cDNA encoding the IFT88 subunit of the IFT particle and identified a Chlamydomonas insertional mutant that is missing this gene. The phenotype of this mutant is normal except for the complete absence of flagella. IFT88 is homologous to mouse and human genes called Tg737. Mice with defects in Tg737 die shortly after birth from polycystic kidney disease. We show that the primary cilia in the kidney of Tg737 mutant mice are shorter than normal. This indicates that IFT is important for primary cilia assembly in mammals. It is likely that primary cilia have an important function in the kidney and that defects in their assembly can lead to polycystic kidney disease.
Figures

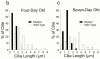
References
-
- Afzelius B.A. The immotile-cilia syndrome and other ciliary diseases. Int. Rev. Exp. Pathol. 1979;19:1–43. - PubMed
-
- Andrews P.M., Porter K.R. A scanning electron microscopic study of the nephron. Am. J. Anat. 1974;140:81–116. - PubMed
-
- Baccetti B., Burrini A.G., Capitani S., Collodel G., Moretti E., Piomboni P., Renieri T. Notulae seminologicae. 2. The ‘short tail’ and ‘stump’ defect in human spermatozoa. Andrologia. 1993;25:331–335. - PubMed
-
- Barr M.M., Sternberg P.W. A polycistic kidney-disease gene homologue required for male mating behaviour in C. elegans . Nature. 1999;401:386–389. - PubMed
-
- Beech P.L., Pagh-Roehl K., Noda Y., Hirokawa N., Burnside B., Rosenbaum J.L. Localization of kinesin superfamily proteins to the connecting cilium of fish photoreceptors. J. Cell Sci. 1996;109:889–897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

