C-Reactive protein binds to apoptotic cells, protects the cells from assembly of the terminal complement components, and sustains an antiinflammatory innate immune response: implications for systemic autoimmunity
- PMID: 11067883
- PMCID: PMC2193350
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.192.9.1353
C-Reactive protein binds to apoptotic cells, protects the cells from assembly of the terminal complement components, and sustains an antiinflammatory innate immune response: implications for systemic autoimmunity
Erratum in
- J Exp Med 2001 Jun 18;193(12):1439
Abstract
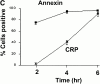
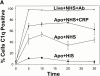
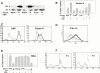
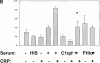
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a serum protein that is massively induced as part of the innate immune response to infection and tissue injury. As CRP has been detected in damaged tissues and is known to activate complement, we assessed whether apoptotic lymphocytes bound CRP and determined the effect of binding on innate immunity. CRP bound to apoptotic cells in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner and augmented the classical pathway of complement activation but protected the cells from assembly of the terminal complement components. Furthermore, CRP enhanced opsonization and phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages associated with the expression of the antiinflammatory cytokine transforming growth factor beta. The antiinflammatory effects of CRP required C1q and factor H and were not effective once cells had become necrotic. These observations demonstrate that CRP and the classical complement components act in concert to promote noninflammatory clearance of apoptotic cells and may help to explain how deficiencies of the classical pathway and certain pentraxins lead to impaired handling of apoptotic cells and increased necrosis with the likelihood of immune response to self.
Figures









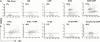

References
-
- Ren Y., Savill J. Apoptosisthe importance of being eaten. Cell. Death. Differ. 1998;5:563–568. - PubMed
-
- Gregory C.D. CD14-dependent clearance of apoptotic cellsrelevance to the immune system. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2000;12:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Gewurz H., Mold C., Siegel J., Fiedel B. C-reactive protein and the acute phase response. Adv. Int. Med. 1982;27:345–372. - PubMed
-
- Steel D.M., Whitehead A.S. The major acute phase reactantsC-reactive protein, serum amyloid P component and serum amyloid A protein. Immunol. Today. 1994;15:81–88. - PubMed
-
- Szalai A.J., Agrawal A., Greenhough T.J., Volanakis J.E. C-reactive protein. Structural biology, gene expression and host defense function. Immunol. Res. 1997;16:127–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

