Regulation of apoptosis at cell division by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of survivin
- PMID: 11069302
- PMCID: PMC27185
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.240390697
Regulation of apoptosis at cell division by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of survivin
Abstract
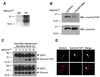
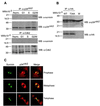
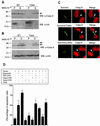
The interface between apoptosis (programmed cell death) and the cell cycle is essential to preserve homeostasis and genomic integrity. Here, we show that survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis over-expressed in cancer, physically associates with the cyclin-dependent kinase p34(cdc2) on the mitotic apparatus, and is phosphorylated on Thr(34) by p34(cdc2)-cyclin B1, in vitro and in vivo. Loss of phosphorylation on Thr(34) resulted in dissociation of a survivin-caspase-9 complex on the mitotic apparatus, and caspase-9-dependent apoptosis of cells traversing mitosis. These data identify survivin as a mitotic substrate of p34(cdc2)-cyclin B1 and suggest that survivin phosphorylation on Thr(34) may be required to preserve cell viability at cell division. Manipulation of this pathway may facilitate the elimination of cancer cells at mitosis.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

