Ssn6-Tup1 interacts with class I histone deacetylases required for repression
- PMID: 11069890
- PMCID: PMC317033
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.829100
Ssn6-Tup1 interacts with class I histone deacetylases required for repression
Abstract
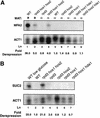
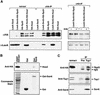
Ssn6-Tup1 regulates multiple genes in yeast, providing a paradigm for corepressor functions. Tup1 interacts directly with histones H3 and H4, and mutation of these histones synergistically compromises Ssn6-Tup1-mediated repression. In vitro, Tup1 interacts preferentially with underacetylated isoforms of H3 and H4, suggesting that histone acetylation may modulate Tup1 functions in vivo. Here we report that histone hyperacetylation caused by combined mutations in genes encoding the histone deacetylases (HDACs) Rpd3, Hos1, and Hos2 abolishes Ssn6-Tup1 repression. Unlike HDAC mutations that do not affect repression, this combination of mutations causes concomitant hyperacetylation of both H3 and H4. Strikingly, two of these class I HDACs interact physically with Ssn6-Tup1. These findings suggest that Ssn6-Tup1 actively recruits deacetylase activities to deacetylate adjacent nucleosomes and promote Tup1-histone interactions.
Figures

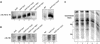
References
-
- Allis CD, Glover CV, Bowen JK, Gorovsky MA. Histone variants specific to the transcriptionally active, amitotically dividing macronucleus of the unicellular eucaryote, Tetrahymena thermophila. Cell. 1980;20:609–617. - PubMed
-
- Bartel PL, Fields S. Analyzing protein–protein interactions using two-hybrid system. Methods Enzymol. 1995;254:241–263. - PubMed
-
- Brownell JE, Allis CD. Special HATs for special occasions: Linking histone acetylation to chromatin assembly and gene activation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996;6:176–184. - PubMed
-
- Carlson M. Genetics of transcriptional regulation in yeast: Connections to the RNA polymerase II CTD. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1997;13:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Carmen AA, Rundlett SE, Grunstein M. HDA1 and HDA3 are components of a yeast histone deacetylase (HDA) complex. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:15837–15844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
