Context-dependent EKLF responsiveness defines the developmental specificity of the human epsilon-globin gene in erythroid cells of YAC transgenic mice
- PMID: 11069894
- PMCID: PMC317038
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.822500
Context-dependent EKLF responsiveness defines the developmental specificity of the human epsilon-globin gene in erythroid cells of YAC transgenic mice
Abstract
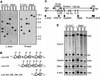
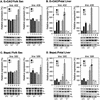
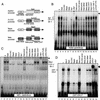
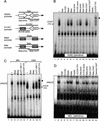
We explored the mechanism of definitive-stage epsilon-globin transcriptional inactivity within a human beta-globin YAC expressed in transgenic mice. We focused on the globin CAC and CAAT promoter motifs, as previous laboratory and clinical studies indicated a pivotal role for these elements in globin gene activation. A high-affinity CAC-binding site for the erythroid krüppel-like factor (EKLF) was placed in the epsilon-globin promoter at a position corresponding to that in the adult beta-globin promoter, thereby simultaneously ablating a direct repeat (DR) element. This mutation led to EKLF-independent epsilon-globin transcription during definitive erythropoiesis. A second 4-bp substitution in the epsilon-globin CAAT sequence, which simultaneously disrupts a second DR element, further enhanced ectopic definitive erythroid activation of epsilon-globin transcription, which surprisingly became EKLF dependent. We finally examined factors in nuclear extracts prepared from embryonic or adult erythroid cells that bound these elements in vitro, and we identified a novel DR-binding protein (DRED) whose properties are consistent with those expected for a definitive-stage epsilon-globin repressor. We conclude that the suppression of epsilon-globin transcription during definitive erythropoiesis is mediated by the binding of a repressor that prevents EKLF from activating the epsilon-globin gene.
Figures
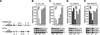


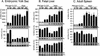

References
-
- Armstrong J, Bieker JJ, Emerson BM. A SWI/SNF-related chromatin remodeling complex, E-RC1, is required for tissue-specific transcriptional regulation by EKLF in vitro. Cell. 1998;95:93–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
