R-Type Ca2+ channels are coupled to the rapid component of secretion in mouse adrenal slice chromaffin cells
- PMID: 11069939
- PMCID: PMC6773200
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-22-08323.2000
R-Type Ca2+ channels are coupled to the rapid component of secretion in mouse adrenal slice chromaffin cells
Abstract
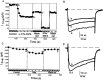
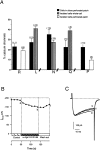
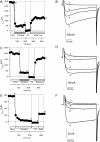
Patch-clamp measurements of Ca(2+) currents and membrane capacitance were performed on slices of mouse adrenal glands, using the perforated-patch configuration of the patch-clamp technique. These recording conditions are much closer to the in vivo situation than those used so far in most electrophysiological studies in adrenal chromaffin cells (isolated cells maintained in culture and whole-cell configuration). We observed profound discrepancies in the quantities of Ca(2+) channel subtypes (P-, Q-, N-, and L-type Ca(2+) channels) described for isolated mouse chromaffin cells maintained in culture. Differences with respect to previous studies may be attributable not only to culture conditions, but also to the patch-clamp configuration used. Our experiments revealed the presence of a Ca(2+) channel subtype never before described in chromaffin cells, a toxin and dihydropyridine-resistant Ca(2+) channel with fast inactivation kinetics, similar to the R-type Ca(2+) channel described in neurons. This channel contributes 22% to the total Ca(2+) current and controls 55% of the rapid secretory response evoked by short depolarizing pulses. Our results indicate that R-type Ca(2+) channels are in close proximity with the exocytotic machinery to rapidly regulate the secretory process.
Figures



References
-
- Albillos A, García A, Gandía L. ω-Agatoxin-IVA-sensitive calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1993;336:259–262. - PubMed
-
- Albillos A, García AG, Olivera B, Gandía L. Re-evaluation of the P/Q Ca2+ channel components of Ba2+ currents in bovine chromaffin cells superfused with solutions containing low and high Ba2+ concentrations. Pflügers Arch. 1996;432:1030–1038. - PubMed
-
- Aosaki T, Kasai H. Characterization of two kinds of high-voltage-activated Ca-channel currents in chick sensory neurons. Differential sensitivity to dihydropyridines and ω-conotoxin GVIA. Pflügers Arch. 1989;414:150–156. - PubMed
-
- Artalejo CR, Perlman RL, Fox AP. ω-Conotoxin GVIA blocks a Ca2+ current in chromaffin cells that is not of the “classic” N Type. Neuron. 1992;8:85–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
