Intrinsic membrane properties underlying spontaneous tonic firing in neostriatal cholinergic interneurons
- PMID: 11069957
- PMCID: PMC6773196
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-22-08493.2000
Intrinsic membrane properties underlying spontaneous tonic firing in neostriatal cholinergic interneurons
Abstract
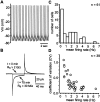
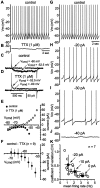
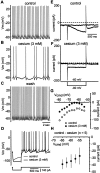
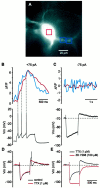
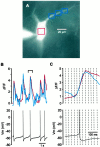
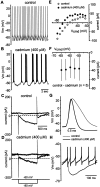
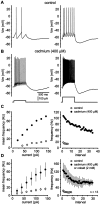
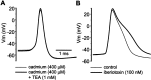
Neostriatal cholinergic interneurons produce spontaneous tonic firing in the absence of synaptic input. Perforated patch recording and whole-cell recording combined with calcium imaging were used in vitro to identify the intrinsic membrane properties underlying endogenous excitability. Spontaneous firing was driven by the combined action of a sodium current and the hyperpolarization-activated cation current (I(h)), which together ensured that there was no zero current point in the subthreshold voltage range. Blockade of sodium channels or I(h) established a stable subthreshold resting membrane potential. A tetrodotoxin-sensitive region of negative slope conductance was observed between approximately -60 mV and threshold (approximately -50 mV) and the h-current was activated at all subthreshold voltages. Calcium imaging experiments revealed that there was minimal calcium influx at subthreshold membrane potentials but that action potentials produced elevations of calcium in both the soma and dendrites. Spike-triggered calcium entry shaped the falling phase of the action potential waveform and activated calcium-dependent potassium channels. Blockade of big-conductance channels caused spike broadening. Application of apamin, which blocks small-conductance channels, abolished the slow spike afterhyperpolarization (AHP) and caused a transition to burst firing. In the absence of synaptic input, a range of tonic firing patterns are observed, suggesting that the characteristic spike sequences described for tonically active cholinergic neurons (TANs) recorded in vivo are intrinsic in origin. The pivotal role of the AHP in regulating spike patterning indicates that burst firing of TANs in vivo could arise from direct or indirect modulation of the AHP without requiring phasic synaptic input.
Figures
References
-
- Adams PR, Constanti A, Brown DA, Clark RB. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982;296:746–749. - PubMed
-
- Aghajanian GK, Rasmussen K. Intracellular studies in the facial nucleus illustrating a simple new method for obtaining viable motoneurons in adult rat brain slices. Synapse. 1989;3:331–338. - PubMed
-
- Akaike N, Harata N. Nystatin perforated patch recording and its applications to analyses of intracellular mechanisms. Jpn J Physiol. 1994;44:433–473. - PubMed
-
- Aosaki T, Graybiel AM, Kimura M. Effect of the nigrostriatal dopamine system on acquired neural responses in the striatum of behaving monkeys. Science. 1994a;265:412–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
