Neuroprotective role of dopamine against hippocampal cell death
- PMID: 11069974
- PMCID: PMC6773169
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-22-08643.2000
Neuroprotective role of dopamine against hippocampal cell death
Abstract
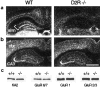
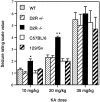
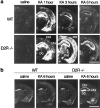
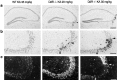
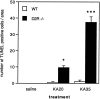
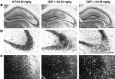
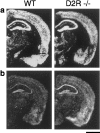
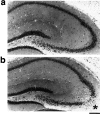
Glutamate excitotoxicity plays a key role in the induction of neuronal cell death occurring in many neuropathologies, including epilepsy. Systemic administration of the glutamatergic agonist kainic acid (KA) is a well characterized model to study epilepsy-induced brain damage. KA-evoked seizures in mice result in hippocampal cell death, with the exception of some strains that are resistant to KA excitotoxicity. Little is known about the factors that prevent epilepsy-related neurodegeneration. Here we show that dopamine has such a function through the activation of the D2 receptor (D2R). D2R gene inactivation confers susceptibility to KA excitotoxicity in two mouse strains known to be resistant to KA-induced neurodegeneration. D2R-/- mice develop seizures when administered KA doses that are not epileptogenic for wild-type (WT) littermates. The spatiotemporal pattern of c-fos and c-jun mRNA induction well correlates with the occurrence of seizures in D2R-/- mice. Moreover, KA-induced seizures result in extensive hippocampal cell death in D2R-/- but not WT mice. In KA-treated D2R-/- mice, hippocampal neurons die by apoptosis, as indicated by the presence of fragmented DNA and the induction of the proapoptotic protein BAX. These results reveal a central role of D2Rs in the inhibitory control of glutamate neurotransmission and excitotoxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Amano T, Ujihara H, Matsubayashi H, Sasa M, Yokota T, Tamura Y, Akaike A. Dopamine-induced protection of striatal neurons against kainate receptor-mediated glutamate cytotoxicity in vitro. Brain Res. 1994;655:61–69. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG, Witter MP. Hippocampal formation. In: Paxinos G, editor. The rat nervous system. Academic; San Diego: 1995. pp. 215–237.
-
- Baik JH, Picetti R, Saiardi A, Thiriet G, Dierich A, Depaulis A, Le Meur M, Borrelli E. Parkinsonian-like locomotor impairment in mice lacking dopamine D2 receptors. Nature. 1995;377:424–428. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Limbic seizures and brain damage produced by kainic acid: mechanisms and relevance to human temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscience. 1985;14:375–403. - PubMed
-
- Berger M, Ben-Ari Y. Autoradiographic visualization of [3H]kainic acid receptor subtypes in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1983;39:237–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
