The vaccinia virus soluble alpha/beta interferon (IFN) receptor binds to the cell surface and protects cells from the antiviral effects of IFN
- PMID: 11070021
- PMCID: PMC113220
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.23.11230-11239.2000
The vaccinia virus soluble alpha/beta interferon (IFN) receptor binds to the cell surface and protects cells from the antiviral effects of IFN
Abstract
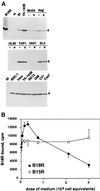
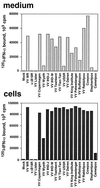
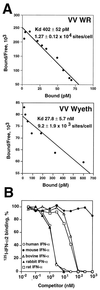
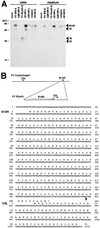
Poxviruses encode a broad range of proteins that interfere with host immune functions, such as soluble versions of receptors for the cytokines tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1 beta, gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), IFN-alpha/beta, and chemokines. These virus-encoded cytokine receptors have a profound effect on virus pathogenesis and enable the study of the role of cytokines in virus infections. The vaccinia virus (VV) Western Reserve gene B18R encodes a secreted protein with 3 immunoglobulin domains that functions as a soluble receptor for IFN-alpha/beta. We have found that after secretion B18R binds to both uninfected and infected cells. The B18R protein present at the cell surface maintains the properties of the soluble receptor, binding IFN-alpha/beta with high affinity and with broad species specificity, and protects cells from the antiviral state induced by IFN-alpha/beta. VV strain Wyeth expressed a truncated B18R protein lacking the C-terminal immunoglobulin domain. This protein binds IFN with lower affinity and retains its ability to bind to cells, indicating that the C-terminal region of B18R contributes to IFN binding. The replication of a VV B18R deletion mutant in tissue culture was restricted in the presence of IFN-alpha, whereas the wild-type virus replicated normally. Binding of soluble recombinant B18R to cells protected the cultures from IFN and allowed VV replication. This represents a novel strategy of virus immune evasion in which secreted IFN-alpha/beta receptors not only bind the soluble cytokine but also bind to uninfected cells and protect them from the antiviral effects of IFN-alpha/beta, maintaining the cells' susceptibility to virus infections. The adaptation of this soluble receptor to block IFN-alpha/beta activity locally will help VV to replicate in the host and spread in tissues. This emphasizes the importance of local effects of IFN-alpha/beta against virus infections.
Figures




References
-
- Alcamí A, Khanna A, Paul N L, Smith G L. Vaccinia virus strains Lister, USSR and Evans express soluble and cell-surface tumour necrosis factor receptors. J Gen Virol. 1999;80:949–959. - PubMed
-
- Alcamí A, Smith G L. A soluble receptor for interleukin-1β encoded by vaccinia virus: a novel mechanism of virus modulation of the host response to infection. Cell. 1992;71:153–167. - PubMed
-
- Beattie E, Tartaglia J, Paoletti E. Vaccinia-virus encoded eIF-2α homolog abrogates the antiviral effect of interferon. Virology. 1991;183:419–422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

