Differential role for competitive reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and intracellular cytokine staining as diagnostic tools for the assessment of intragraft cytokine profiles in rejecting and nonrejecting heart allografts
- PMID: 11073805
- PMCID: PMC1885719
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64783-9
Differential role for competitive reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and intracellular cytokine staining as diagnostic tools for the assessment of intragraft cytokine profiles in rejecting and nonrejecting heart allografts
Abstract
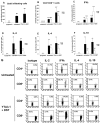
The early and reliable diagnosis of allograft rejection is a difficult task and the assessment of cytokine expression in the grafts can be a helpful parameter. We have compared competitive reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) with intracellular cytokine staining by flow cytometry as tools to measure cytokine expression in rejecting and nonrejecting murine cardiac allografts. Both techniques gave comparable results for cytokine expression in rejecting allografts and syngeneic controls. Grafts from mice pretreated with anti-CD4 antibody and donor-specific blood transfusion showed a marked reduction in cytokine expression, as assessed by competitive RT-PCR, even though a cellular infiltrate was present in the graft. In contrast, the cytokine production measured by intracellular cytokine staining of the isolated graft-infiltrating cells was high and exceeded even that of the rejecting allografts. We conclude that intracellular cytokine staining of graft-infiltrating leukocytes by flow cytometry does not necessarily reflect accurately the cytokine milieu in the graft. This technique might therefore have a limited clinical application in contrast to competitive RT-PCR for the differentiation between graft acceptance and graft rejection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cytokine mRNA profiles in mouse orthotopic liver transplantation. Graft rejection is associated with augmented TH1 function.Transplantation. 1995 Jan 27;59(2):274-81. Transplantation. 1995. PMID: 7530874
-
Predominant expression of Th2 cytokines and interferon-gamma in xenogeneic cardiac grafts undergoing acute vascular rejection.Transplantation. 2003 Mar 15;75(5):586-90. doi: 10.1097/01.TP.0000052594.83318.68. Transplantation. 2003. PMID: 12640294
-
Increased expression of IL-4 and IL-10 and decreased expression of IL-2 and interferon-gamma in long-surviving mouse heart allografts after brief CD4-monoclonal antibody therapy.Transplantation. 1995 Feb 27;59(4):559-65. Transplantation. 1995. PMID: 7878761
-
In vivo depletion of CD8+ T cells results in Th2 cytokine production and alternate mechanisms of allograft rejection.Transplantation. 1995 Apr 27;59(8):1155-61. Transplantation. 1995. PMID: 7732563
-
Interferon-gamma-secreting T-cell populations in rejecting murine cardiac allografts: assessment by flow cytometry.Am J Pathol. 1998 Nov;153(5):1383-92. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65725-2. Am J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9811329 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CD4+ T lymphocytes are not necessary for the acute rejection of vascularized mouse lung transplants.J Immunol. 2008 Apr 1;180(7):4754-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.7.4754. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18354199 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basadonna GP, Matas AJ, Gillingham KJ, Payne WD, Dunn DL, Sutherland DE, et al: Early versus late acute renal allograft rejection: impact on chronic rejection. Transplantation 1993, 55:993-995 - PubMed
-
- Forbes RD, Rowan RA, Billingham ME: Endocardial infiltrates in human heart transplants: a serial biopsy analysis comparing four immunosuppression protocols. Hum Pathol 1990, 21:850-855 - PubMed
-
- Suzuki J, Isobe M, Yamazaki S, Horie S, Okubo Y, Sekiguchi M: Sensitive diagnosis of cardiac allograft rejection by detection of cytokine transcription in situ. Cardiovasc Res 1998, 40:307-313 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

