Inducible metabolism of phenolic acids in Pediococcus pentosaceus is encoded by an autoregulated operon which involves a new class of negative transcriptional regulator
- PMID: 11073918
- PMCID: PMC111416
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.23.6724-6731.2000
Inducible metabolism of phenolic acids in Pediococcus pentosaceus is encoded by an autoregulated operon which involves a new class of negative transcriptional regulator
Abstract
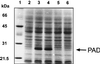
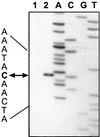
Pediococcus pentosaceus displays a substrate-inducible phenolic acid decarboxylase (PAD) activity on p-coumaric acid. Based on DNA sequence homologies between the three PADs previously cloned, a DNA probe of the Lactobacillus plantarum pdc gene was used to screen a P. pentosaceus genomic library in order to clone the corresponding gene of this bacteria. One clone detected with this probe displayed a low PAD activity. Subcloning of this plasmid insertion allowed us to determine the part of the insert which contains a 534-bp open reading frame (ORF) coding for a 178-amino-acid protein presenting 81.5% of identity with L. plantarum PDC enzyme. This ORF was identified as the padA gene. A second ORF was located just downstream of the padA gene and displayed 37% identity with the product of the Bacillus subtilis yfiO gene. Subcloning, transcriptional analysis, and expression studies with Escherichia coli of these two genes under the padA gene promoter, demonstrated that the genes are organized in an autoregulated bicistronic operonic structure and that the gene located upstream of the padA gene encodes the transcriptional repressor of the padA gene. Transcription of this pad operon in P. pentosaceus is acid phenol dependent.
Figures


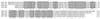


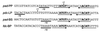

References
-
- Adler K, Beyreuther K, Geisler N, Gronenborn B, Klemm A, Muller-Hill B, Pfahl M, Schmitz A. How lac repressor binds to DNA. Nature. 1972;237:322–327. - PubMed
-
- Alekshun M N, Levy S B. The mar regulon: multiple resistance to antibiotics and other toxic chemicals. Trends Microbiol. 1999;7:410–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

