Interdependence of activation at rhaSR by cyclic AMP receptor protein, the RNA polymerase alpha subunit C-terminal domain, and rhaR
- PMID: 11073923
- PMCID: PMC111421
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.23.6774-6782.2000
Interdependence of activation at rhaSR by cyclic AMP receptor protein, the RNA polymerase alpha subunit C-terminal domain, and rhaR
Abstract
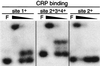
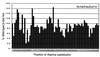
The Escherichia coli rhaSR operon encodes two AraC family transcription activators, RhaS and RhaR, and is activated by RhaR in the presence of L-rhamnose. beta-Galactosidase assays of various rhaS-lacZ promoter fusions combined with mobility shift assays indicated that a cyclic AMP receptor protein (CRP) site located at -111.5 is also required for full activation of rhaSR expression. To address the mechanisms of activation by CRP and the RNA polymerase alpha-subunit C-terminal domain (alpha-CTD) at rhaSR, we tested the effects of alanine substitutions in CRP activating regions 1 and 2, overexpression of a truncated version of alpha (alpha-Delta235), and alanine substitutions throughout alpha-CTD. We found that DNA-contacting residues in alpha-CTD are required for full activation, and for simplicity, we discuss alpha-CTD as a third activator of rhaSR. CRP and RhaR could each partially activate transcription in the absence of the other two activators, and alpha-CTD was not capable of activation alone. In the case of CRP, this suggests that this activation involves neither an alpha-CTD interaction nor cooperative binding with RhaR, while in the case of RhaR, this suggests the likelihood of direct interactions with core RNA polymerase. We also found that CRP, RhaR, and alpha-CTD each have synergistic effects on activation by the others, suggesting direct or indirect interactions among all three. We have some evidence that the alpha-CTD-CRP and alpha-CTD-RhaR interactions might be direct. The magnitude of the synergistic effects was usually greater with just two activators than with all three, suggesting possible redundancies in the mechanisms of activation by CRP, alpha-CTD, and RhaR.
Figures


References
-
- Berg O G, von Hippel P H. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. II. The binding specificity of cyclic AMP receptor protein to recognition sites. J Mol Biol. 1988;200:709–723. - PubMed
-
- Blatter E E, Ross W, Tang H, Gourse R L, Ebright R H. Domain organization of RNA polymerase α subunit: C-terminal 85 amino acids constitute a domain capable of dimerization and DNA binding. Cell. 1994;78:889–896. - PubMed
-
- Busby S, Ebright R H. Transcription activation at class II CAP-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1997;23:853–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

