Analysis of cyclin D3-cdk4 complexes in fibroblasts expressing and lacking p27(kip1) and p21(cip1)
- PMID: 11073976
- PMCID: PMC86501
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.23.8748-8757.2000
Analysis of cyclin D3-cdk4 complexes in fibroblasts expressing and lacking p27(kip1) and p21(cip1)
Abstract
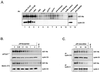
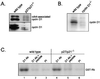
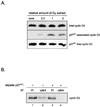
Our studies examined the effects of p27(kip1) and p21(cip1) on the assembly and activity of cyclin D3-cdk4 complexes and determined the composition of the cyclin D3 pool in cells containing and lacking these cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. We found that catalytically active cyclin D3-cdk4 complexes were present in fibroblasts derived from p27(kip1)-p21(cip1)-null mice and that immunodepletion of extracts of wild-type cells with antibody to p27(kip1) and/or p21(cip1) removed cyclin D3 protein but not cyclin D3-associated activity. Similar results were observed in experiments assaying cyclin D1-cdk4 activity. Data obtained using mixed cell extracts demonstrated that p27(kip1) interacted with cyclin D3-cdk4 complexes in vitro and that this interaction was paralleled by a loss of cyclin D3-cdk4 activity. In p27(kip1)-p21(cip1)-deficient cells, the cyclin D3 pool consisted primarily of cyclin D3 monomers, whereas in wild-type cells, the majority of cyclin D3 molecules were complexed to cdk4 and either p27(kip1) or p21(cip1) or were monomeric. We conclude that neither p27(kip1) nor p21(cip1) is required for the formation of cyclin D3-cdk4 complexes and that cyclin D3-cdk4 complexes containing p27(kip1) or p21(cip1) are inactive. We suggest that only a minor portion of the total cyclin D3 pool accounts for all of the cyclin D3-cdk4 activity in the cell regardless of whether the cell contains p27(kip1) and p21(cip1).
Figures


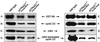


References
-
- Alessi F, Quarta S, Savio M, Riva F, Rossi L, Stivala L A, Scovassi A I, Meijer L, Prosperi E. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors olomoucine and roscovitine arrest human fibroblasts in G1 phase by specific inhibition of CDK2 kinase activity. Exp Cell Res. 1998;245:8–18. - PubMed
-
- Blain S W, Montalvo E, Massague J. Differential interaction of the cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor p27Kip1 with cyclin A-Cdk2 and cyclin D2-Cdk4. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:25863–25872. - PubMed
-
- Brugarolas J, Chandrasekaran C, Gordon J I, Beach D, Jacks T, Hannon G J. Radiation-induced cell cycle arrest compromised by p21 deficiency. Nature. 1995;377:552–557. - PubMed
-
- Carlson B A, Dubay M M, Sausville E A, Brizuela L, Worland P J. Flavopiridol induces G1 arrest with inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 2 and CDK4 in human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1996;56:2973–2978. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
