Novel Upf2p orthologues suggest a functional link between translation initiation and nonsense surveillance complexes
- PMID: 11073994
- PMCID: PMC86549
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.23.8944-8957.2000
Novel Upf2p orthologues suggest a functional link between translation initiation and nonsense surveillance complexes
Abstract
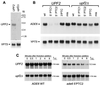
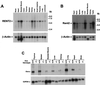
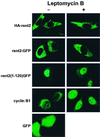
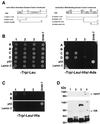
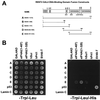
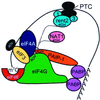
Transcripts harboring premature signals for translation termination are recognized and rapidly degraded by eukaryotic cells through a pathway known as nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). In addition to protecting cells by preventing the translation of potentially deleterious truncated peptides, studies have suggested that NMD plays a broader role in the regulation of the steady-state levels of physiologic transcripts. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, three trans-acting factors (Upf1p to Upf3p) are required for NMD. Orthologues of Upf1p have been identified in numerous species, showing that the NMD machinery, at least in part, is conserved through evolution. In this study, we demonstrate additional functional conservation of the NMD pathway through the identification of Upf2p homologues in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and humans (rent2). Disruption of S. pombe UPF2 established that this gene is required for NMD in fission yeast. rent2 was demonstrated to interact directly with rent1, a known trans-effector of NMD in mammalian cells. Additionally, fragments of rent2 were shown to possess nuclear targeting activity, although the native protein localizes to the cytoplasmic compartment. Finally, novel functional domains of Upf2p and rent2 with homology to eukaryotic initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) and other translational regulatory proteins were identified. Directed mutations within these so-called eIF4G homology (4GH) domains were sufficient to abolish the function of S. pombe Upf2p. Furthermore, using the two-hybrid system, we obtained evidence for direct interaction between rent2 and human eIF4AI and Sui1, both components of the translation initiation complex. Based on these findings, a novel model in which Upf2p and rent2 effects decreased translation and accelerated decay of nonsense transcripts through competitive interactions with eIF4G-binding partners is proposed.
Figures


References
-
- Atkin A L, Schenkman L R, Eastham M, Dahlseid J N, Lelivelt M J, Culbertson M R. Relationship between yeast polyribosomes and Upf proteins required for nonsense mRNA decay. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:22163–22172. - PubMed
-
- Bassett D E, Jr, Boguski M S, Spencer F, Reeves R, Goebl M, Hieter P. Comparative genomics, genome cross-referencing and XREFdb. Trends Genet. 1995;11:372–373. - PubMed
-
- Beelman C A, Parker R. Degradation of mRNA in eukaryotes. Cell. 1995;81:179–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
