Mice with an increased glucocorticoid receptor gene dosage show enhanced resistance to stress and endotoxic shock
- PMID: 11073999
- PMCID: PMC86554
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.23.9009-9017.2000
Mice with an increased glucocorticoid receptor gene dosage show enhanced resistance to stress and endotoxic shock
Abstract
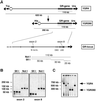
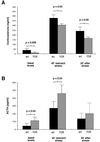
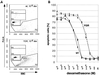
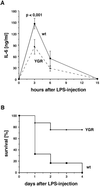
Targeted mutagenesis of the glucocorticoid receptor has revealed an essential function for survival and the regulation of multiple physiological processes. To investigate the effects of an increased gene dosage of the receptor, we have generated transgenic mice carrying two additional copies of the glucocorticoid receptor gene by using a yeast artificial chromosome. Interestingly, overexpression of the glucocorticoid receptor alters the basal regulation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis, resulting in reduced expression of corticotropin-releasing hormone and adrenocorticotrope hormone and a fourfold reduction in the level of circulating glucocorticoids. In addition, primary thymocytes obtained from transgenic mice show an enhanced sensitivity to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Finally, analysis of these mice under challenge conditions revealed that expression of the glucocorticoid receptor above wild-type levels leads to a weaker response to restraint stress and a strongly increased resistance to lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxic shock. These results underscore the importance of tight regulation of glucocorticoid receptor expression for the control of physiological and pathological processes. Furthermore, they may explain differences in the susceptibility of humans to inflammatory diseases and stress, depending on individual prenatal and postnatal experiences known to influence the expression of the glucocorticoid receptor.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Disruption of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical system in transgenic mice expressing type II glucocorticoid receptor antisense ribonucleic acid permanently impairs T cell function: effects on T cell trafficking and T cell responsiveness during postnatal development.Endocrinology. 1995 Sep;136(9):3949-60. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.9.7649104. Endocrinology. 1995. PMID: 7649104
-
Prenatal exposure to dexamethasone alters hippocampal drive on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity in adult male rats.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006 May;290(5):R1366-73. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00757.2004. Epub 2006 Jan 5. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16397092
-
Endocrine profile and neuroendocrine challenge tests in transgenic mice expressing antisense RNA against the glucocorticoid receptor.Neuroendocrinology. 1997 Sep;66(3):212-20. doi: 10.1159/000127240. Neuroendocrinology. 1997. PMID: 9380279
-
Early environmental regulation of forebrain glucocorticoid receptor gene expression: implications for adrenocortical responses to stress.Dev Neurosci. 1996;18(1-2):49-72. doi: 10.1159/000111395. Dev Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8840086 Review.
-
When not enough is too much: the role of insufficient glucocorticoid signaling in the pathophysiology of stress-related disorders.Am J Psychiatry. 2003 Sep;160(9):1554-65. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.160.9.1554. Am J Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12944327 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of dietary corticosterone on the central adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway in broiler chickens.J Anim Sci. 2020 Jul 1;98(7):skaa202. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa202. J Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32599620 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of corticosterone and dietary energy on immune function of broiler chickens.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 24;10(3):e0119750. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119750. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25803644 Free PMC article.
-
Increased glucocorticoid receptor expression and activity mediate the LPS resistance of SPRET/EI mice.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 1;285(40):31073-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.154484. Epub 2010 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20663891 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysregulation and behavioral analysis of mouse mutants with altered glucocorticoid or mineralocorticoid receptor function.Stress. 2008 Sep;11(5):321-38. doi: 10.1080/10253890701821081. Stress. 2008. PMID: 18609295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in developmental programming of health and disease.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2013 Jan;34(1):27-46. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2012.11.002. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23200813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ashwell J D, Lu F W, Vacchio M S. Glucocorticoids in T cell development and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:309–345. - PubMed
-
- Barnes P J. Anti-inflammatory actions of glucocorticoids: molecular mechanisms. Clin Sci. 1998;94:557–572. - PubMed
-
- Burke D T, Carle G F, Olson M V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987;236:806–812. - PubMed
-
- Cohen J J. Glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in the thymus. Semin Immunol. 1992;4:363–369. - PubMed
-
- Cole T J, Blendy J A, Monaghan A P, Krieglstein K, Schmid W, Aguzzi A, Fantuzzi G, Hummler E, Unsicker K, Schütz G. Targeted disruption of the glucocorticoid receptor gene blocks adrenergic chromaffin cell development and severely retards lung maturation. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1608–1621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
