Mutational and structural analyses of the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor Sml1 define its Rnr1 interaction domain whose inactivation allows suppression of mec1 and rad53 lethality
- PMID: 11074005
- PMCID: PMC86560
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.23.9076-9083.2000
Mutational and structural analyses of the ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor Sml1 define its Rnr1 interaction domain whose inactivation allows suppression of mec1 and rad53 lethality
Abstract
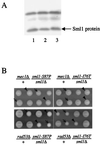
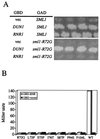
In budding yeast, MEC1 and RAD53 are essential for cell growth. Previously we reported that mec1 or rad53 lethality is suppressed by removal of Sml1, a protein that binds to the large subunit of ribonucleotide reductase (Rnr1) and inhibits RNR activity. To understand further the relationship between this suppression and the Sml1-Rnr1 interaction, we randomly mutagenized the SML1 open reading frame. Seven mutations were identified that did not affect protein expression levels but relieved mec1 and rad53 inviability. Interestingly, all seven mutations abolish the Sml1 interaction with Rnr1, suggesting that this interaction causes the lethality observed in mec1 and rad53 strains. The mutant residues all cluster within the 33 C-terminal amino acids of the 104-amino-acid-long Sml1 protein. Four of these residues reside within an alpha-helical structure that was revealed by nuclear magnetic resonance studies. Moreover, deletions encompassing the N-terminal half of Sml1 do not interfere with its RNR inhibitory activity. Finally, the seven sml1 mutations also disrupt the interaction with yeast Rnr3 and human R1, suggesting a conserved binding mechanism between Sml1 and the large subunit of RNR from different species.
Figures




References
-
- Adams A, Gottschling D E, Kaiser C A, Stearns T. Methods in yeast genetics, a Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory course manual. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1997.
-
- Bell D W, Varley J M, Szydlo T E, Kang D H, Wahrer D C, Shannon K E, Lubratovich M, Verselis S J, Isselbacher K J, Fraumeni J F, Birch J M, Li F P, Garber J E, Haber D A. Heterozygous germ line hCHK2 mutations in Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Science. 1999;286:2528–2531. - PubMed
-
- Caspari T. How to activate p53. Curr Biol. 2000;10:R315–R317. - PubMed
-
- Chabes A, Domkin V, Thelander L. Yeast Sml1, a protein inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:36679–36683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
