Haplotypes at ATM identify coding-sequence variation and indicate a region of extensive linkage disequilibrium
- PMID: 11078475
- PMCID: PMC1287921
- DOI: 10.1086/316908
Haplotypes at ATM identify coding-sequence variation and indicate a region of extensive linkage disequilibrium
Abstract
Genetic variation in the human population may lead to functional variants of genes that contribute to risk for common chronic diseases such as cancer. In an effort to detect such possible predisposing variants, we constructed haplotypes for a candidate gene and tested their efficacy in association studies. We developed haplotypes consisting of 14 biallelic neutral-sequence variants that span 142 kb of the ATM locus. ATM is the gene responsible for the autosomal recessive disease ataxia-telangiectasia (AT). These ATM noncoding single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were genotyped in nine CEPH families (89 individuals) and in 260 DNA samples from four different ethnic origins. Analysis of these data with an expectation-maximization algorithm revealed 22 haplotypes at this locus, with three major haplotypes having frequencies > or = .10. Tests for recombination and linkage disequilibrium (LD) show reduced recombination and extensive LD at the ATM locus, in all four ethnic groups studied. The most striking example was found in the study population of European ancestry, in which no evidence for recombination could be discerned. The potential of ATM haplotypes for detection of genetic variants through association studies was tested by analysis of 84 individuals carrying one of three ATM coding SNPs. Each coding SNP was detected by association with an ATM haplotype. We demonstrate that association studies with haplotypes for candidate genes have significant potential for the detection of genetic backgrounds that contribute to disease.
Figures



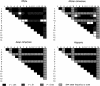
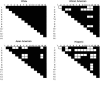
Comment in
-
Resolving ATM haplotypes in whites.Am J Hum Genet. 2003 Apr;72(4):1071-3. doi: 10.1086/373879. Am J Hum Genet. 2003. PMID: 12708462 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GenBank Overview, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/GenbankOverview.html (for genomic sequence [accession number U82828])
References
-
- Boerwinkle E, Ellsworth DL, Hallman DM, Biddinger A (1996) Genetic analysis of atherosclerosis: a research paradigm for the common chronic diseases. Hum Mol Genet 5:1405–1410 - PubMed
-
- Cargill M, Altshuler D, Ireland J, Sklar P, Ardlie K, Patil N, Shaw N, Lane CR, Lim EP, Kalyanaraman N, Nemesh J, Ziaugra L, Friedland L, Rolfe A, Warrington J, Lipshutz R, Daley GQ, Lander ES (1999) Characterization of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in coding regions of human genes. Nat Genet 22:231–238 (erratum: Nat Genet 23:373 [1999]) - PubMed
-
- Collins FS, Guyer MS, Charkravarti A (1997) Variations on a theme: cataloging human DNA sequence variation. Science 278:1580–1581 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

