Eukaryotic chaperonin CCT stabilizes actin and tubulin folding intermediates in open quasi-native conformations
- PMID: 11080144
- PMCID: PMC305829
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.22.5971
Eukaryotic chaperonin CCT stabilizes actin and tubulin folding intermediates in open quasi-native conformations
Abstract
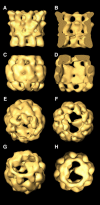
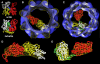
Three-dimensional reconstruction from cryoelectron micrographs of the eukaryotic cytosolic chaperonin CCT complexed to tubulin shows that CCT interacts with tubulin (both the alpha and beta isoforms) using five specific CCT subunits. The CCT-tubulin interaction has a different geometry to the CCT-actin interaction, and a mixture of shared and unique CCT subunits is used in binding the two substrates. Docking of the atomic structures of both actin and tubulin to their CCT-bound conformation suggests a common mode of chaperonin-substrate interaction. CCT stabilizes quasi-native structures in both proteins that are open through their domain-connecting hinge regions, suggesting a novel mechanism and function of CCT in assisted protein folding.
Figures



References
-
- Archibald J.M., Logdson,J.M. and Doolittle,W.F. (2000) Origin and evolution of eukaryotic chaperonins. Phylogenetic evidence for ancient duplications in CCT genes. Mol. Biol. Evol., 17, 1456–1466. - PubMed
-
- Bosch G., Baumeister,W. and Essen,L.O. (2000) Crystal structure of the β-apical domain of the thermosome reveals structural plasticity in the protrusion region. J. Mol. Biol., 301, 19–25. - PubMed
-
- Braig K. Otwinowski,Z., Hegde,R., Boisvert,D.C., Joachimiak,A., Horwich,A.L. and Sigler,P.B. (1994) The crystal structure of the bacterial chaperonin GroEL at 2.8 Å. Nature, 371, 578–586. - PubMed
-
- Brunger A.T. et al. (1998) Crystallography and NMR System (CNS): a new software system for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D, 54, 905–921. - PubMed
-
- Bukau B. and Horwich,A.L. (1998) The hsp70 and hsp60 chaperone machines. Cell, 92, 351–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

