Phosphorylation and N-terminal region of yeast ribosomal protein P1 mediate its degradation, which is prevented by protein P2
- PMID: 11080154
- PMCID: PMC305824
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.22.6075
Phosphorylation and N-terminal region of yeast ribosomal protein P1 mediate its degradation, which is prevented by protein P2
Abstract
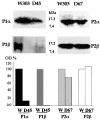
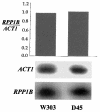
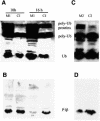
The stalk proteins P1 and P2, which are fundamental for ribosome activity, are the only ribosomal components for which there is a cytoplasmic pool. Accumulation of these two proteins is differentially regulated in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by degradation. In the absence of P2, the amount of P1 is drastically reduced; in contrast, P2 proteins are not affected by a deficiency in P1. However, association with P2 protects P1 proteins. The half-life of P1 is a few minutes, while that of P2 is several hours. The proteasome is not involved in the degradation of P1 proteins. The different sensitivity to degradation of these two proteins is associated with two structural features: phosphorylation and N-terminus structure. A phosphorylation site at the C-terminus is required for P1 proteolysis. P2 proteins, despite being phosphorylated, are protected by their N-terminal peptide. An exchange of the first five amino acids between the two types of protein makes P1 resistant and P2 sensitive to degradation.
Figures




References
-
- Ballesta J.P.G. and Remacha,M. (1996) The large ribosomal subunit stalk as a regulatory element of the eukaryotic translational machinery. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol., 55, 157–193. - PubMed
-
- Ballesta J.P.G., Guarinos,E., Zurdo,J., Parada,P., Nusspaumer,G., Lalioti,V.S., Perez-Fernandez,J. and Remacha,M. (2000) Structure of the yeast ribosomal stalk. In Garrett,R., Douthwaite,S., Matheson,A., Liljas,A., Moore,P.B. and Noller,H.F. (eds), The Ribosome. Structure, Function, Antibiotics and Cellular Interactions. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp. 115–125.
-
- Bonneaud N., Ozier-Kalogeropoulos,O., Li,G.Y., Labouesse,M., Minvielle-Sebastia,L. and Lacroute,F. (1991) A family of low and high copy replicative, integrative and single-stranded S. cerevisiae/E. coli shuttle vectors. Yeast, 7, 609–615. - PubMed
-
- Broach J., Strathern,J.N. and Hicks,J.B. (1979) Transformation in yeast: development of a hybrid cloning vector and isolation of the CAN1 gene. Gene, 8, 121–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

