Pathophysiological and protective roles of mitochondrial ion channels
- PMID: 11080248
- PMCID: PMC2270186
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00023.x
Pathophysiological and protective roles of mitochondrial ion channels
Abstract
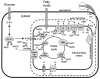
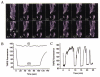
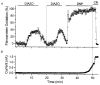
Mitochondria possess a highly permeable outer membrane and an inner membrane that was originally thought to be relatively impermeable to ions to prevent dissipation of the electrochemical gradient for protons. Although recent evidence has revealed a rich diversity of ion channels in both membranes, the purpose of these channels remains incompletely determined. Pores in the outer membrane are fundamental participants in apoptotic cell death, and this process may also involve permeability transition pores on the inner membrane. Novel functions are now being assigned to other ion channels of the inner membrane. Examples include protection against ischaemic injury by mitochondrial KATP channels and the contribution of inner membrane anion channels to spontaneous mitochondrial oscillations in cardiac myocytes. The central role of mitochondria in both the normal function of the cell and in its demise makes these channels prime targets for future research and drug development.
Figures
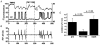
References
-
- Antonenko YN, Kinnally KW, Tedeschi H. Identification of anion and cation pathways in the inner mitochondrial membrane by patch clamping of mouse liver mitoplasts. Journal of Membrane Biology. 1991;124:151–158. - PubMed
-
- Auchampach JA, Grover GJ, Gross GJ. Blockade of ischaemic preconditioning in dogs by the novel ATP dependent potassium channel antagonist sodium 5-hydroxydecanoate. Cardiovascular Research. 1992;26:1054–1062. - PubMed
-
- Ballarin C, Sorgato MC. An electrophysiological study of yeast mitochondria. Evidence for two inner membrane anion channels sensitive to ATP. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1995;270:19262–19268. - PubMed
-
- Beavis AD. Properties of the inner membrane anion channel in intact mitochondria. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes. 1992;24:77–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

