Molecular determinant for run-down of L-type Ca2+ channels localized in the carboxyl terminus of the 1C subunit
- PMID: 11080256
- PMCID: PMC2270188
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00119.x
Molecular determinant for run-down of L-type Ca2+ channels localized in the carboxyl terminus of the 1C subunit
Abstract
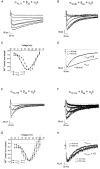
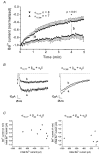
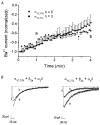
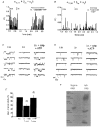
1. The role of the sequence 1572-1651 in the C-terminal tail of the alpha1C subunit in run-down of Ca2+ channels was studied by comparing functional properties of the conventional alpha1C,77 channel with those of three isoforms carrying alterations in this motif. 2. The pore-forming alpha1C subunits were co-expressed with alpha2delta and beta2a subunits in HEK-tsA201 cells, a subclone of the human embryonic kidney cell line, and studied by whole-cell and single-channel patch-clamp techniques. 3. Replacement of amino acids 1572-1651 in alpha1C,77 with 81 different amino acids leading to alpha1C,86 significantly altered run-down behaviour. Run-down of Ba2+ currents was rapid with alpha1C,77 channels, but was slow with alpha1C,86. 4. Transfer of the alpha1C,86 segments L (amino acids 1572-1598) or K (amino acids 1595-1652) into the alpha1C,77 channel yielded alpha1C,77L and alpha1C,77K channels, respectively, the run-down of which resembled more that of alpha1C,77. These results demonstrate that a large stretch of sequence between residues 1572 and 1652 of alpha1C,86 renders Ca2+ channels markedly resistant to run-down. 5. The protease inhibitor calpastatin added together with ATP was able to reverse the run-down of alpha1C,77 channels. Calpastatin expression was demonstrated in the HEK-tsA cells by Western blot analysis. 6. These results indicate a significant role of the C-terminal sequence 1572-1651 of the alpha1C subunit in run-down of L-type Ca2+ channels and suggest this sequence as a target site for a modulatory effect by endogenous calpastatin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Complexes of the alpha1C and beta subunits generate the necessary signal for membrane targeting of class C L-type calcium channels.J Biol Chem. 1999 Jan 22;274(4):2137-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.4.2137. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 9890976
-
Modulation of the smooth-muscle L-type Ca2+ channel alpha1 subunit (alpha1C-b) by the beta2a subunit: a peptide which inhibits binding of beta to the I-II linker of alpha1 induces functional uncoupling.Biochem J. 2000 Jun 15;348 Pt 3(Pt 3):657-65. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10839999 Free PMC article.
-
Crucial role of N terminus in function of cardiac L-type Ca2+ channel and its modulation by protein kinase C.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jul 10;273(28):17901-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.28.17901. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9651396
-
Molecular structures involved in L-type calcium channel inactivation. Role of the carboxyl-terminal region encoded by exons 40-42 in alpha1C subunit in the kinetics and Ca2+ dependence of inactivation.J Biol Chem. 1997 Feb 7;272(6):3560-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.6.3560. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9013606
-
Action of calpastatin in prevention of cardiac L-type Ca2+ channel run-down cannot be mimicked by synthetic calpain inhibitors.Pflugers Arch. 1995 Feb;429(4):503-10. doi: 10.1007/BF00704155. Pflugers Arch. 1995. PMID: 7617440
Cited by
-
Atherosclerosis-related molecular alteration of the human CaV1.2 calcium channel alpha1C subunit.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 7;103(45):17024-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606539103. Epub 2006 Oct 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17071743 Free PMC article.
-
Atrial fibrillation: basic mechanisms, remodeling and triggers.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2005 Sep;13(3):181-93. doi: 10.1007/s10840-005-2362-y. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2005. PMID: 16177845 Review. No abstract available.
-
Modulation of the voltage sensor of L-type Ca2+ channels by intracellular Ca2+.J Gen Physiol. 2004 May;123(5):555-71. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200308876. J Gen Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15111645 Free PMC article.
-
Long range correlations of the ion current in SV channels. Met3PbCl influence study.PLoS One. 2020 Mar 3;15(3):e0229433. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229433. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32126096 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical properties of a conventional calcium channel beta subunit from the platyhelminth Schistosoma mansoni.BMC Physiol. 2008 Mar 26;8:6. doi: 10.1186/1472-6793-8-6. BMC Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18366784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belles B, Hescheler J, Trautwein W, Blomgren K, Karlsson JO. A possible physiological role of the Ca-dependent protease calpain and its inhibitor calpastatin on the Ca2+ current in guinea pig myocytes. Pflügers Archiv. 1988a;412:554–556. - PubMed
-
- Belles B, Malecot CO, Hescheler J, Trautwein W. Run-down’ of the Ca current during whole-cell recordings in guinea pig heart cells: role of phosporylation and intracellular Ca2+ Pflügers Archiv. 1988b;411:353–360. - PubMed
-
- Catterall WA. Structure and function of voltage-gated ion channels. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 1995;64:493–531. - PubMed
-
- Cavalie A, Ochi R, Pelzer D, Trautwein W. Elementary currents through Ca2+ channels in guinea pig myocytes. Pflügers Archiv. 1983;398:284–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

