Modular domain structure of Arabidopsis COP1. Reconstitution of activity by fragment complementation and mutational analysis of a nuclear localization signal in planta
- PMID: 11080276
- PMCID: PMC59198
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.124.3.979
Modular domain structure of Arabidopsis COP1. Reconstitution of activity by fragment complementation and mutational analysis of a nuclear localization signal in planta
Abstract
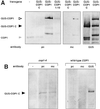
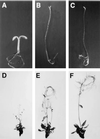
The Arabidopsis COP1 protein functions as a developmental regulator, in part by repressing photomorphogenesis in darkness. Using complementation of a cop1 loss-of-function allele with transgenes expressing fusions of cop1 mutant proteins and beta-glucuronidase, it was confirmed that COP1 consists of two modules, an amino terminal module conferring a basal function during development and a carboxyl terminal module conferring repression of photomorphogenesis. The amino-terminal zinc-binding domain of COP1 was indispensable for COP1 function. In contrast, the debilitating effects of site-directed mutations in the single nuclear localization signal of COP1 were partially compensated by high-level transgene expression. The carboxyl-terminal module of COP1, though unable to substantially ameliorate a cop1 loss-of-function allele on its own, was sufficient for conferring a light-quality-dependent hyperetiolation phenotype in the presence of wild-type COP1. Moreover, partial COP1 activity could be reconstituted in vivo from two non-covalently linked, complementary polypeptides that represent the two functional modules of COP1. Evidence is presented for efficient association of the two sub-fragments of the split COP1 protein in Arabidopsis and in a yeast two-hybrid assay.
Figures

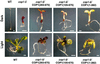


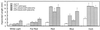

References
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Struhl K. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. New York: New York Greene Publishing/Wiley Interscience; 1997.
-
- Clough SJ, Bent AF. Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998;16:735–743. - PubMed
-
- Deng X-W, Caspar T, Quail PH. cop1: a regulatory locus involved in light-controlled development and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 1991;5:1172–1182. - PubMed
-
- Deng X-W, Matsui M, Wei N, Wagner D, Chu AM, Feldmann KA, Quail PH. COP1, an Arabidopsis regulatory gene, encodes a novel protein with both a Zn-binding motif and a Gβ homologous domain. Cell. 1992;71:791–801. - PubMed
-
- Fankhauser C, Chory J. Light control of plant development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:203–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

