Selective opioid agonist and antagonist competition for [3H]-naloxone binding in amphibian spinal cord
- PMID: 11082500
- PMCID: PMC3062938
- DOI: 10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02967-x
Selective opioid agonist and antagonist competition for [3H]-naloxone binding in amphibian spinal cord
Abstract
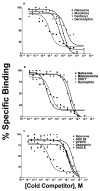
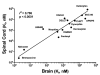
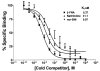
Opioids elicit antinociception in mammals through three distinct types of receptors designated as mu, kappa and delta. However, it is not clear what type of opioid receptor mediates antinociception in non-mammalian vertebrates. Radioligand binding techniques were employed to characterize the site(s) of opioid action in the amphibian, Rana pipiens. Naloxone is a general opioid antagonist that has not been characterized in Rana pipiens. Using the non-selective opioid antagonist, [3H]-naloxone, opioid binding sites were characterized in amphibian spinal cord. Competitive binding assays were done using selective opioid agonists and highly-selective opioid antagonists. Naloxone bound to a single-site with an affinity of 11.3 nM and 18.7 nM for kinetic and saturation studies, respectively. A B(max) value of 2725 fmol/mg protein in spinal cord was observed. The competition constants (K(i)) of unlabeled mu, kappa and delta ranged from 2.58 nM to 84 microM. The highly-selective opioid antagonists yielded similar K(i) values ranging from 5.37 to 31.1 nM. These studies are the first to examine opioid binding in amphibian spinal cord. In conjunction with previous behavioral data, these results suggest that non-mammalian vertebrates express a unique opioid receptor which mediates the action of selective mu, kappa and delta opioid agonists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Selective opioid receptor agonist and antagonist displacement of [3H]naloxone binding in amphibian brain.Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Jun 2;397(2-3):255-62. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(00)00265-x. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10844122
-
Opioid receptor ligands in the neonatal rat spinal cord: binding and in vitro depression of the nociceptive responses.Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):503-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12958.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1990. PMID: 2158845 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of multiple kappa-opioid receptors by selective and nonselective ligand binding in guinea pig spinal cord: resolution of high and low affinity states of the kappa 2 receptors by a computerized model-fitting technique.Mol Pharmacol. 1990 May;37(5):694-703. Mol Pharmacol. 1990. PMID: 2160061
-
Opioid research in amphibians: an alternative pain model yielding insights on the evolution of opioid receptors.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2004 Oct;46(2):204-15. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.07.003. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2004. PMID: 15464208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for the existence of the beta-endorphin-sensitive "epsilon-opioid receptor" in the brain: the mechanisms of epsilon-mediated antinociception.Jpn J Pharmacol. 1998 Mar;76(3):233-53. doi: 10.1254/jjp.76.233. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9593217 Review.
Cited by
-
The evolution of vertebrate opioid receptors.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(4):1247-69. doi: 10.2741/3306. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19273128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single Amino Acid Variation Underlies Species-Specific Sensitivity to Amphibian Skin-Derived Opioid-like Peptides.Chem Biol. 2015 Jun 18;22(6):764-75. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.05.012. Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 26091169 Free PMC article.
-
Xendorphin B1, a novel opioid-like peptide determined from a Xenopus laevis brain cDNA library, produces opioid antinociception after spinal administration in amphibians.Brain Res Bull. 2007 Mar 30;71(6):628-32. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2006.12.001. Epub 2007 Jan 4. Brain Res Bull. 2007. PMID: 17292806 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of buprenorphine and butorphanol analgesia in the eastern red-spotted newt (Notophthalmus viridescens).J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2009 Mar;48(2):171-5. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2009. PMID: 19383214 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic and spinal administration of the mu opioid, remifentanil, produces antinociception in amphibians.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Mar 18;534(1-3):89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.01.011. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16487509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benyhe S, Varga E, Hepp J, Magyar A, Borsodi A, Wollemann M. Characterization of kappa1 and kappa2 opioid binding sites in frog (Rana esculenta) brain membrane. Neurochem. Res. 1990;15:899–904. - PubMed
-
- Benyhe S, Wollemann M. Ethylketocyclazocine and N-cyclopropylmethyl-norazidomorphine are antagonists of morphine-induced analgesia in frog spinal cord. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988;37:555–556. - PubMed
-
- Blurton PA, Broadhurst AM, Wood MD, Wyllie MG. Is there a common, high-affinity opioid binding site in rat brain? J. Recept. Res. 1986;6:85–93. - PubMed
-
- Broadbear JH, Negus SS, Butelman ER, De Costa BR, Woods JH. Differential effects of systemically administered nor-binaltorphimine (nor-BNI) on kappa-opioid agonists in the mouse writhing assay. Psychopharmacology. 1994;115:311–319. - PubMed
-
- Buatti MC, Pasternak GW. Multiple opiate receptors: phylogenetic differences. Brain Res. 1981;218:400–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

