Comparative In vitro activities of daptomycin and vancomycin against resistant gram-positive pathogens
- PMID: 11083657
- PMCID: PMC90222
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.12.3447-3450.2000
Comparative In vitro activities of daptomycin and vancomycin against resistant gram-positive pathogens
Abstract
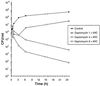
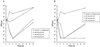
The in vitro activity of daptomycin against 224 current gram-positive clinical isolates including vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium (VREF), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus spp. (MRSS), and penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae (PRSP) was evaluated. The MICs at which 90% of isolates are inhibited for daptomycin and vancomycin, respectively, were as follows: MRSA, 1 and 2 microg/ml; MRSS, 1 and 4 microg/ml; PRSP, 1 and 0.5 microg/ml; and VREF, 2 and >64 microg/ml. Daptomycin was bactericidal against 82% of 17 VREF isolates. The antibacterial activity of daptomycin was strongly dependent on the calcium concentration of the medium. Daptomycin was active against all gram-positive cocci tested.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro effect of the presence of human albumin or human serum on the bactericidal activity of daptomycin against strains with the main resistance phenotypes in Gram-positives.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007 Jun;59(6):1185-9. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkm078. Epub 2007 Apr 5. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17412725
-
Bactericidal activities of two daptomycin regimens against clinical strains of glycopeptide intermediate-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model with simulated endocardial vegetations.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001 Feb;45(2):454-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.45.2.454-459.2001. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11158740 Free PMC article.
-
The in vitro activity of daptomycin against 514 Gram-positive aerobic clinical isolates.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2001 Aug;48(2):219-23. doi: 10.1093/jac/48.2.219. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2001. PMID: 11481291
-
Evaluation of in vitro activity of quinupristin/dalfopristin and comparator antimicrobial agents against worldwide clinical trial and other laboratory isolates.Am J Med. 1998 May 29;104(5A):34S-42S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(98)00153-3. Am J Med. 1998. PMID: 9684656 Review.
-
A current perspective on daptomycin for the clinical microbiologist.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013 Oct;26(4):759-80. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00030-13. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 24092854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Baseline study to determine in vitro activities of daptomycin against gram-positive pathogens isolated in the United States in 2000-2001.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 May;47(5):1689-93. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.5.1689-1693.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12709341 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of daptomycin in experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 May;47(5):1714-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.5.1714-1718.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12709345 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotics for treatment of resistant gram-positive coccal infections.Indian J Pediatr. 2006 Apr;73(4):323-34. doi: 10.1007/BF02825827. Indian J Pediatr. 2006. PMID: 16816494 Review.
-
Treatment options for vancomycin-resistant enterococcal infections.Drugs. 2002;62(3):425-41. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262030-00002. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 11827558 Review.
-
Identification of Clostridioides difficile mutants with increased daptomycin resistance.J Bacteriol. 2024 Mar 21;206(3):e0036823. doi: 10.1128/jb.00368-23. Epub 2024 Feb 20. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38376203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benson C A, Beaudette F, Trenholm G. Comparative in vitro activity of LY146032, a new peptide, with vancomycin and eight other agents against gram-positive organisms. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987;20:191–196. - PubMed
-
- Hanberger H, Nilsson L E, Maller R, Isaksson B. Pharmacodynamics of daptomycin and vancomycin on E. faecalis and S. aureus demonstrated by studies of initial killing and postantibiotic effect and influence of Ca2+ and albumin on these drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991;35:1710–1716. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lakey J H, Ptak M. Fluorescence indicates a calcium-dependent interaction between the lipopeptide antibiotic LY 146032 and phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1988;27:4639–4645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

