Differential removal of thymidine nucleotide analogues from blocked DNA chains by human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase in the presence of physiological concentrations of 2'-deoxynucleoside triphosphates
- PMID: 11083661
- PMCID: PMC90226
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.12.3465-3472.2000
Differential removal of thymidine nucleotide analogues from blocked DNA chains by human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase in the presence of physiological concentrations of 2'-deoxynucleoside triphosphates
Abstract
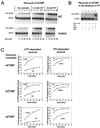
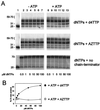
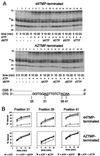
Removal of 2',3'-didehydro-3'-deoxythymidine-5'-monophosphate (d4TMP) from a blocked DNA chain can occur through transfer of the chain-terminating residue to a nucleotide acceptor by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase (RT). ATP-dependent removal of either d4TMP or 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine-5'-monophosphate (AZTMP) is increased in AZT resistant HIV-1 RT (containing D67N/K70R/T215F/K219Q mutations). Removal of d4TMP is strongly inhibited by the next complementary deoxynucleoside triphosphate (50% inhibitory concentration [IC(50)] of approximately 0.5 microM), whereas removal of AZTMP is much less sensitive to this inhibition (IC(50) of >100 microM). This could explain the lack of cross-resistance by AZT-resistant HIV-1 to d4T in phenotypic drug susceptibility assays.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multidrug-resistant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: involvement of ribonucleotide-dependent phosphorolysis in cross-resistance to nucleoside analogue inhibitors.J Mol Biol. 2002 Oct 18;323(2):181-97. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00911-7. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12381314
-
Enhanced binding of azidothymidine-resistant human immunodeficiency virus 1 reverse transcriptase to the 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine 5'-monophosphate-terminated primer.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 5;273(23):14596-604. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.23.14596. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9603976
-
Nucleoside analog resistance caused by insertions in the fingers of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase involves ATP-mediated excision.J Virol. 2002 Sep;76(18):9143-51. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.18.9143-9151.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12186898 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-steady-state kinetic characterization of wild type and 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase: implication of RNA directed DNA polymerization in the mechanism of AZT resistance.Biochemistry. 1997 Nov 18;36(46):14064-70. doi: 10.1021/bi9713862. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9369478
-
Inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and fidelity of in vitro DNA replication.J Enzyme Inhib. 1992;6(1):35-46. doi: 10.3109/14756369209041354. J Enzyme Inhib. 1992. PMID: 1285301 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel genetic pathway of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 resistance to stavudine mediated by the K65R mutation.J Virol. 2003 May;77(10):5685-93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.10.5685-5693.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12719561 Free PMC article.
-
The M184V mutation reduces the selective excision of zidovudine 5'-monophosphate (AZTMP) by the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1.J Virol. 2002 Apr;76(7):3248-56. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.7.3248-3256.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11884549 Free PMC article.
-
A Guide to HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase and Protease Sequencing for Drug Resistance Studies.HIV Seq Compend. 2001;2001:1-51. HIV Seq Compend. 2001. PMID: 22324021 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Nucleocapsid Protein Precursors NCp9 and NCp15 Suppress ATP-Mediated Rescue of AZT-Terminated Primers by HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Sep 21;64(10):e00958-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00958-20. Print 2020 Sep 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32747359 Free PMC article.
-
ATP-dependent removal of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Jul;46(7):2179-84. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.7.2179-2184.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 12069972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arion D, Kaushik N, McCormick S, Borkow G, Parniak M A. Phenotypic mechanism of HIV-1 resistance to 3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine (AZT): increased polymerization processivity and enhanced sensitivity to pyrophosphate of the mutant viral reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry. 1998;37:15908–15917. - PubMed
-
- Battula N, Loeb L A. On the fidelity of DNA replication: lack of exodeoxyribonuclease activity and error-correction function in avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1976;251:982–986. - PubMed
-
- Braylan R C, Fowlkes B J, Jaffe E S, Sanders S K, Berard C W, Herman C J. Cell volumes and DNA distributions of normal and neoplastic human lymphoid cells. Cancer. 1978;41:201–209. - PubMed
-
- Carroll S S, Geib J, Olsen D B, Stahlhut M, Shafer J A, Kuo L C. Sensitivity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and its mutants to inhibition by azidothymidine triphosphate. Biochemistry. 1994;33:2113–2120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

