Haemodynamic and hormonal effects of adrenomedullin in patients with pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 11083748
- PMCID: PMC1729511
- DOI: 10.1136/heart.84.6.653
Haemodynamic and hormonal effects of adrenomedullin in patients with pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether infusion of adrenomedullin, a potent vasorelaxant peptide, has beneficial haemodynamic and hormonal effects in patients with pulmonary hypertension.
Patients and design: The haemodynamic and hormonal responses to intravenous infusion of adrenomedullin (0.05 microgram/kg/min) or placebo were examined in 13 patients with precapillary pulmonary hypertension.
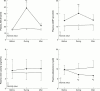
Results: Infusion of adrenomedullin produced a 44% increase in cardiac index (mean (SD) 1.8 (0.2) to 2.6 (0.3) l/min/m(2), p < 0. 05) and a 32% decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance (19.7 (1.4) to 13.4 (1.3) units, p < 0.05), with a 4% reduction in mean pulmonary arterial pressure (62 (4) to 59 (4) mm Hg, NS). Adrenomedullin also decreased mean systemic arterial pressure (81 (3) to 72 (4) mm Hg, p < 0.05) and increased heart rate (73 (4) to 79 (4) beats/min, p < 0.05). Adrenomedullin decreased plasma aldosterone (9.8 (2.5) to 7.1 (1.5) ng/dl, p < 0.05) without significant changes in plasma renin activity. Plasma atrial and brain natriuretic peptides tended to decrease with adrenomedullin, although these changes did not reach significance. The haemodynamic and hormonal variables remained unchanged during placebo infusion.
Conclusions: Intravenous adrenomedullin has beneficial haemodynamic and hormonal effects in patients with precapillary pulmonary hypertension.
Figures

Comment in
-
Adrenomedullin in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension.Heart. 2000 Dec;84(6):575-6. doi: 10.1136/heart.84.6.575. Heart. 2000. PMID: 11083724 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
