Capsule impedes adhesion to and invasion of epithelial cells by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 11083790
- PMCID: PMC97775
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.12.6744-6749.2000
Capsule impedes adhesion to and invasion of epithelial cells by Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
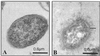
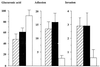
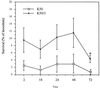
The adhesion of K21a, K26, K36, and K50 capsulated Klebsiella strains to ileocecal (HCT-8) and bladder (T24) epithelial cell lines was significantly lower than that of their corresponding spontaneous noncapsulated variants K21a/3, K26/1, K36/3, and K50/3, respectively. Internalization of the bacteria by both epithelial cell lines was also significantly reduced. Similarly, a capsule-switched derivative, K2(K36), that exhibited a morphologically larger K36 capsule and formed more capsular material invaded the ileocecal epithelial cell line poorly compared to the corresponding K2 parent strain. None of the capsulated strains exhibited significant mannose-sensitive type 1 fimbriae, whereas two of the noncapsulated variants K21a/3 and K50/3 exhibited potent mannose-sensitive hemagglutinating activity. Although hemagglutinating activity that could be attributed to mannose-resistant Klebsiella type 3 fimbriae was weak in all strains, in several cases the encapsulated parent strains exhibited lower titers than their corresponding noncapsulated variants. Although the level of adhesion to the ileocecal cells is not different from adhesion to bladder cells, bacterial internalization by bladder cells was significantly lower than internalization by ileocecal cells, suggesting that bladder cells lack components required for the internalization of Klebsiella.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Consequences of reduction of Klebsiella pneumoniae capsule expression on interactions of this bacterium with epithelial cells.Infect Immun. 1999 Feb;67(2):554-61. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.2.554-561.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 9916058 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships among capsular structure, phagocytosis, and mouse virulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae.Infect Immun. 1995 Mar;63(3):847-52. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.3.847-852.1995. Infect Immun. 1995. PMID: 7868255 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic exchange of determinants for capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis between Klebsiella pneumoniae strains expressing serotypes K2 and K21a.Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4208-16. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4208-4216.1993. Infect Immun. 1993. PMID: 8104896 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the humoral immune response to Klebsiella species in inflammatory bowel disease and ankylosing spondylitis.Br J Rheumatol. 1998 May;37(5):525-31. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.5.525. Br J Rheumatol. 1998. PMID: 9651080
-
SP-A enhances phagocytosis of Klebsiella by interaction with capsular polysaccharides and alveolar macrophages.Am J Physiol. 1997 Feb;272(2 Pt 1):L344-52. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1997.272.2.L344. Am J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9124386
Cited by
-
cjrABC-senB hinders survival of extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli in the bloodstream through triggering complement-mediated killing.J Biomed Sci. 2020 Aug 6;27(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12929-020-00677-4. J Biomed Sci. 2020. PMID: 32762693 Free PMC article.
-
First Report of Potentially Pathogenic Klebsiella pneumoniae from Serotype K2 in Mollusk Tegillarca granosa and Genetic Diversity of Klebsiella pneumoniae in 14 Species of Edible Aquatic Animals.Foods. 2022 Dec 15;11(24):4058. doi: 10.3390/foods11244058. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36553800 Free PMC article.
-
Manno(rhamno)biose-containing capsular polysaccharides of Klebsiella pneumoniae enhance opsono-stimulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes.J Innate Immun. 2009;1(2):136-44. doi: 10.1159/000154812. Epub 2008 Sep 9. J Innate Immun. 2009. PMID: 20375572 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of bacterial surface polysaccharides by lectins of the innate immune system and its contribution to defense against infection: the case of pulmonary pathogens.Infect Immun. 2008 Apr;76(4):1322-32. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00910-07. Epub 2007 Dec 17. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18086817 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Inosine and D-Mannose Secreted by Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Affect Viability of Lung Epithelial Cells.Molecules. 2022 May 6;27(9):2994. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092994. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blumenkrantz N, Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973;54:484–489. - PubMed
-
- Campbell W, Hendrix E, Cryz S J, Cross A. Immunogenicity of a 24-valent Klebsiella capsular polysaccharide vaccine and an eight-valent Pseudomonas O-polysaccharide conjugate vaccine administered to victims of acute trauma. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;23:179–181. - PubMed
-
- Casewell M, Talsania H G. Predominance of certain Klebsiella capsular types in hospitals in the United Kingdom. J Infect. 1979;1:77–79.
-
- Cryz S J, Jr, Fürer E, Germanier R. Safety and immunogenicity of Klebsiella pneumoniae K1 capsular polysaccharide vaccine in humans. J Infect Dis. 1985;151:665–671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

