Hemin-binding surface protein from Bartonella quintana
- PMID: 11083791
- PMCID: PMC97776
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.12.6750-6757.2000
Hemin-binding surface protein from Bartonella quintana
Abstract
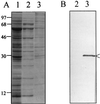
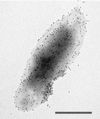
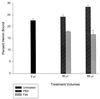
Bartonella quintana, the agent of trench fever and a cause of endocarditis and bacillary angiomatosis in humans, has the highest reported in vitro hemin requirement for any bacterium. We determined that eight membrane-associated proteins from B. quintana bind hemin and that a approximately 25-kDa protein (HbpA) was the dominant hemin-binding protein. Like many outer membrane proteins, HbpA partitions to the detergent phase of a Triton X-114 extract of the cell and is heat modifiable, displaying an apparent molecular mass shift from approximately 25 to 30 kDa when solubilized at 100 degrees C. Immunoblots of purified outer and inner membranes and immunoelectron microscopy with whole cells show that HbpA is strictly located in the outer membrane and surface exposed, respectively. The N-terminal sequence of mature HbpA was determined and used to clone the HbpA-encoding gene (hbpA) from a lambda genomic library. The hbpA gene is 816 bp in length, encoding a predicted immature protein of approximately 29.3 kDa and a mature protein of 27.1 kDa. A Fur box homolog with 53% identity to the Escherichia coli Fur consensus is located upstream of hbpA and may be involved in regulating expression. BLAST searches indicate that the closest homologs to HbpA include the Bartonella henselae phage-associated membrane protein, Pap31 (58.4% identity), and the OMP31 porin from Brucella melitensis (31.7% identity). High-stringency Southern blots indicate that all five pathogenic Bartonella spp. possess hbpA homologs. Recombinant HbpA can bind hemin in vitro; however, it does not confer a hemin-binding phenotype upon E. coli. Intact B. quintana treated with purified anti-HbpA Fab fragments show a significant (P < 0.004) dose-dependent decrease in hemin binding relative to controls, suggesting that HbpA plays an active role in hemin acquisition and therefore pathogenesis. HbpA is the first potential virulence determinant characterized from B. quintana.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Environmental signals generate a differential and coordinated expression of the heme receptor gene family of Bartonella quintana.Infect Immun. 2006 Jun;74(6):3251-61. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00245-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16714552 Free PMC article.
-
Five-member gene family of Bartonella quintana.Infect Immun. 2003 Feb;71(2):814-21. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.2.814-821.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12540561 Free PMC article.
-
Function, regulation, and transcriptional organization of the hemin utilization locus of Bartonella quintana.Infect Immun. 2009 Jan;77(1):307-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01194-08. Epub 2008 Nov 3. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 18981245 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillary angiomatosis in immunocompromised patients.AIDS. 1998 Oct 1;12(14):1793-803. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199814000-00011. AIDS. 1998. PMID: 9792380 Review.
-
Bartonella (Rochalimaea) quintana infections.Clin Microbiol Rev. 1996 Jul;9(3):273-92. doi: 10.1128/CMR.9.3.273. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1996. PMID: 8809460 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Environmental signals generate a differential and coordinated expression of the heme receptor gene family of Bartonella quintana.Infect Immun. 2006 Jun;74(6):3251-61. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00245-06. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16714552 Free PMC article.
-
Brucella melitensis omp31 Mutant Is Attenuated and Confers Protection Against Virulent Brucella melitensis Challenge in BALB/c Mice.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Apr 28;30(4):497-504. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1908.08056. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31986561 Free PMC article.
-
Hemin-binding proteins as potent markers for serological diagnosis of infections with Bartonella quintana.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013 Apr;20(4):620-6. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00717-12. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23408526 Free PMC article.
-
The Bartonella quintana extracytoplasmic function sigma factor RpoE has a role in bacterial adaptation to the arthropod vector environment.J Bacteriol. 2013 Jun;195(11):2662-74. doi: 10.1128/JB.01972-12. Epub 2013 Apr 5. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23564167 Free PMC article.
-
Heme degrading protein HemS is involved in oxidative stress response of Bartonella henselae.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037630. Epub 2012 May 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22701524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Anderson B, Goldsmith C, Johnson A, Padmalayam I, Baumstark B. Bacteriophage-like particle from Rochalimaea henselae. Mol Microbiol. 1994;13:67–73. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1995.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

