Interleukin-1 receptor type I gene-deficient mice are less susceptible to Staphylococcus epidermidis biomaterial-associated infection than are wild-type mice
- PMID: 11083815
- PMCID: PMC97800
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.12.6924-6931.2000
Interleukin-1 receptor type I gene-deficient mice are less susceptible to Staphylococcus epidermidis biomaterial-associated infection than are wild-type mice
Abstract
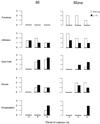
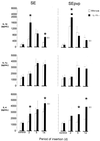
Elevated concentrations of interleukin-1 (IL-1) were found in tissue surrounding biomaterials infected with Staphylococcus epidermidis. To determine the role of IL-1 in biomaterial-associated infection (BAI), IL-1 receptor type I-deficient (IL-1R(-/-)) and wild-type mice received subcutaneous implants of silicon elastomer (SE) or polyvinylpyrrolidone-grafted SE (SEpvp), combined with an injection of 10(6) CFU of S. epidermidis or sterile saline. Neither mouse strain was susceptible to BAI around SE. IL-1R(-/-) mice with SEpvp implants had a no abscess formation and a reduced susceptibility to persistent S. epidermidis infection. The normal foreign body response, characterized by giant-cell formation and encapsulation, was delayed around SEpvp in wild-type mice but not in IL-1R(-/-) mice. This coincided with enhanced local IL-4 production in IL-1R(-/-) mice. These data suggest that inhibition of local IL-1 activity may be beneficial for the outcome of BAI.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enhanced susceptibility to subcutaneous abscess formation and persistent infection around catheters is associated with sustained interleukin-1beta levels.Infect Immun. 2000 Mar;68(3):1692-5. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.3.1692-1695.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10678990 Free PMC article.
-
Peri-implant tissue is an important niche for Staphylococcus epidermidis in experimental biomaterial-associated infection in mice.Infect Immun. 2007 Mar;75(3):1129-36. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01262-06. Epub 2006 Dec 11. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17158900 Free PMC article.
-
Subcutaneous abscess formation around catheters induced by viable and nonviable Staphylococcus epidermidis as well as by small amounts of bacterial cell wall components.J Biomed Mater Res. 2000 Jun 15;50(4):546-56. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4636(20000615)50:4<546::aid-jbm10>3.0.co;2-y. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000. PMID: 10756313
-
Biomaterial-associated persistence of Staphylococcus epidermidis in pericatheter macrophages.J Infect Dis. 2000 Apr;181(4):1337-49. doi: 10.1086/315369. Epub 2000 Apr 13. J Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 10762565
-
Interactions between the foreign body reaction and Staphylococcus aureus biomaterial-associated infection. Winning strategies in the derby on biomaterial implant surfaces.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2022 Sep;48(5):624-640. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2021.2011132. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34879216 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-1β Promotes Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms on Implants in vivo.Front Immunol. 2019 May 17;10:1082. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01082. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31156635 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial-Specific Induction of Inflammatory Cytokines Significantly Decreases upon Dual Species Infections of Implant Materials with Periodontal Pathogens in a Mouse Model.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 26;10(2):286. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020286. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203495 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Chemokine System in Tissue Response to Prosthetic By-products Leading to Periprosthetic Osteolysis and Aseptic Loosening.Front Immunol. 2017 Aug 24;8:1026. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01026. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28883822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic Mechanisms and Host Interactions in Staphylococcus epidermidis Device-Related Infection.Front Microbiol. 2017 Aug 2;8:1401. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01401. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28824556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The type 1 interleukin-1 receptor is essential for the efficient activation of microglia and the induction of multiple proinflammatory mediators in response to brain injury.J Neurosci. 2002 Jul 15;22(14):6071-82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-14-06071.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12122068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiura K, Gelfand J A, Wakabayashi G, Callahan M, Burke J F, Thomson J, Dinarello C A. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist blocks Staphylococcal induced shock in rabbits. Cytokine. 1991;3:498.
-
- Anderson J M. Inflammatory response to implants. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1988;34:101–107. - PubMed
-
- Arend W, Malyak M, Guthridge C, Gabay C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist: role in biology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:27–55. - PubMed
-
- Bach A, Bohrer H, Motsch J, Martin E, Geiss H K, Sonntag H G. Prevention of catheter-related infections by antiseptic bonding. J Surg Res. 1993;55:640–646. - PubMed
-
- Bisno A, Waldvogel F. Infections associated with indwelling medical devices. 2nd ed. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology; 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

