Surface protein variation by expression site switching in the relapsing fever agent Borrelia hermsii
- PMID: 11083837
- PMCID: PMC97822
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.12.7114-7121.2000
Surface protein variation by expression site switching in the relapsing fever agent Borrelia hermsii
Abstract
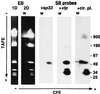
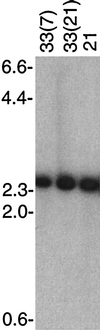
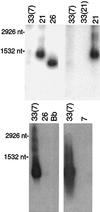
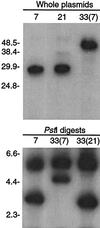
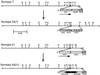
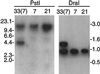
Borrelia hermsii, an agent of relapsing fever, undergoes antigenic variation of serotype-specifying membrane proteins during mammalian infections. When B. hermsii is cultivated in broth medium, one serotype, 33, eventually predominates in the population. Serotype 33 has also been found to be dominant in ticks but not in mammalian hosts. We investigated the biology and genetics of two independently derived clonal populations of serotype 33 of B. hermsii. Both isolates infected immunodeficient mice, but serotype 33 cells were limited in number and were only transiently present in the blood. Probes for vsp33, which encodes the serotype-specifying Vsp33 outer membrane protein, revealed that the gene was located on a 53-kb linear plasmid and that there was only one locus for the gene in serotype 33. The vsp33 probe and probes for other variable membrane protein genes showed that expression of Vsp33 was determined at the level of transcription and that when the vsp33 expression site was active, an expression site for other variable proteins was silent. The study confirmed that serotype 33 is distinct from other serotypes of B. hermsii in its biology and demonstrated that B. hermsii can change its major surface protein through switching between two expression sites.
Figures
References
-
- Barbour A G. Antigenic variation of a relapsing fever Borrelia species. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:155–171. - PubMed
-
- Barbour A G. Linear DNA of Borrelia species and antigenic variation. Trends Microbiol. 1993;1:236–239. - PubMed
-
- Barbour A G, Burman N, Carter C J, Kitten T, Bergstrom S. Variable antigen genes of the relapsing fever agent Borrelia hermsii are activated by promoter addition. Mol Microbiol. 1991;5:489–493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

