Localization of dysfunctional tight junctions in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium-infected epithelial layers
- PMID: 11083857
- PMCID: PMC97842
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.12.7202-7208.2000
Localization of dysfunctional tight junctions in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium-infected epithelial layers
Abstract
Infection of polarized MDCK epithelial layers by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is accompanied by increased tight junction permeability and by contraction of perijunctional actinomyosin. We localized dysfunctional tight junctions in serovar Typhimurium-infected MDCK layers by imaging apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion of fluorescent lipid and found that loss of the apical-basolateral diffusion barrier (tight junction fence function) was most marked in areas of prominent perijunctional contraction. The protein kinase inhibitor staurosporine prevented perijunctional contraction but did not reverse the effects of serovar Typhimurium on tight junction barrier function. Hence, perijunctional contraction is not required for Salmonella-induced tight junction dysfunction and this epithelial response to infection may be multifactorial.
Figures
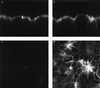
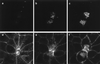

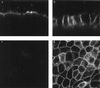
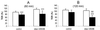
Similar articles
-
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium effectors SopB, SopE, SopE2 and SipA disrupt tight junction structure and function.Cell Microbiol. 2006 Dec;8(12):1946-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00762.x. Epub 2006 Jul 26. Cell Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16869830
-
Disruption of epithelial barrier integrity by Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium requires geranylgeranylated proteins.Infect Immun. 2003 Feb;71(2):872-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.2.872-881.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12540569 Free PMC article.
-
The Gli1-Snail axis contributes to Salmonella Typhimurium-induced disruption of intercellular junctions of intestinal epithelial cells.Cell Microbiol. 2020 Aug;22(8):e13211. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13211. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Cell Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32329192
-
Tight junctions.J Cell Sci. 1998 Mar;111 ( Pt 5):541-7. doi: 10.1242/jcs.111.5.541. J Cell Sci. 1998. PMID: 9454728 Review.
-
Functional analysis of tight junctions.Methods. 2003 Jul;30(3):228-34. doi: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00029-x. Methods. 2003. PMID: 12798137 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Proteolytic Peptide R7I Protects the Intestinal Barrier and Alleviates Fatty Acid Malabsorption in Salmonella typhimurium-Infected Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 16;24(22):16409. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216409. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003599 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 inhibits leaky gut by enhancing mucosal integrity.PLoS One. 2007 Dec 12;2(12):e1308. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001308. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 18074031 Free PMC article.
-
Disentangling the innate immune responses of intestinal epithelial cells and lamina propria cells to Salmonella Typhimurium infection in chickens.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 3;14:1258796. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1258796. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37854334 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of tight junctions and induction of proinflammatory cytokine responses in colonic epithelial cells by Campylobacter jejuni.Infect Immun. 2006 Dec;74(12):6581-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00958-06. Epub 2006 Oct 2. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 17015453 Free PMC article.
-
Enteric Pathogens and Their Toxin-Induced Disruption of the Intestinal Barrier through Alteration of Tight Junctions in Chickens.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Feb 10;9(2):60. doi: 10.3390/toxins9020060. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28208612 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balda M S, Whitney J A, Flores C, González S, Cereijido M, Matter K. Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J Cell Biol. 1996;134:1031–1049. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brumell J H, Steele-Mortimer O, Finlay B B. Bacterial invasion: force feeding by Salmonella. Curr Biol. 1999;9:R277–R280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

