Association of an odor with activation of olfactory bulb noradrenergic beta-receptors or locus coeruleus stimulation is sufficient to produce learned approach responses to that odor in neonatal rats
- PMID: 11085610
- PMCID: PMC1885991
- DOI: 10.1037/0735-7044.114.5.957
Association of an odor with activation of olfactory bulb noradrenergic beta-receptors or locus coeruleus stimulation is sufficient to produce learned approach responses to that odor in neonatal rats
Abstract
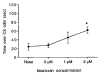
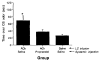
These experiments examined the sufficiency of pairing an odor with either intrabulbar activation of noradrenergic beta-receptors or pharmacological stimulation of the locus coeruleus to support learned odor preferences in Postnatal Day 6-7 rat pups. The results showed that pups exposed to odor paired with beta-receptor activation limited to the olfactory bulb (isoproterenol, 50 microM) displayed a conditioned approach response on subsequent exposure to that odor. Furthermore, putative stimulation of the locus coeruleus (2 microM idazoxan or 2 mM acetylcholine) paired with odor produced a subsequent preference for that odor. The effects of locus coeruleus stimulation could be blocked by a pretraining injection of the beta-receptor antagonist propranolol (20 mg/kg). Together these results suggest that convergence of odor input with norepinephrine release from the locus coeruleus terminals within the olfactory bulb is sufficient to support olfactory learning.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The biphasic effects of locus coeruleus noradrenergic activation on dendrodendritic inhibition in the rat olfactory bulb.Brain Res. 1998 Feb 9;783(2):272-9. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(97)01371-1. Brain Res. 1998. PMID: 9507162
-
Mitral cell beta1 and 5-HT2A receptor colocalization and cAMP coregulation: a new model of norepinephrine-induced learning in the olfactory bulb.Learn Mem. 2003 Jan-Feb;10(1):5-15. doi: 10.1101/lm.54803. Learn Mem. 2003. PMID: 12551959 Free PMC article.
-
Norepinephrine and learning-induced plasticity in infant rat olfactory system.J Neurosci. 1989 Nov;9(11):3998-4006. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-11-03998.1989. J Neurosci. 1989. PMID: 2585063 Free PMC article.
-
The neurobiology of infant maternal odor learning.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2010 Oct;43(10):914-9. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2010007500090. Epub 2010 Sep 10. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2010. PMID: 20835686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rodent model of infant attachment learning and stress.Dev Psychobiol. 2010 Nov;52(7):651-60. doi: 10.1002/dev.20482. Dev Psychobiol. 2010. PMID: 20730787 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental neurobiology of the rat attachment system and its modulation by stress.Behav Sci (Basel). 2012 Jun 1;2(2):79-102. doi: 10.3390/bs2020079. Behav Sci (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23626910 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid modulation of Fos protein expression and olfactory circuitry plays a pivotal role in what neonates remember.Learn Mem. 2006 Sep-Oct;13(5):590-8. doi: 10.1101/lm.301206. Learn Mem. 2006. PMID: 17015856 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine inhibits mitral/tufted--> granule cell synapses in the frog olfactory bulb.J Neurosci. 2004 Sep 15;24(37):8057-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2138-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15371506 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated electrical activity in the olfactory bulb gates the oscillatory entrainment of entorhinal networks in neonatal mice.PLoS Biol. 2019 Jan 31;17(1):e2006994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2006994. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 30703080 Free PMC article.
-
Noradrenergic plasticity of olfactory sensory neuron inputs to the main olfactory bulb.J Neurosci. 2014 Nov 12;34(46):15234-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0551-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25392492 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams LM, Foote SL. Effects of locally infused pharmacological agents on spontaneous and sensory-evoked activity of locus coeruleus neurons. Brain Research Bulletin. 1988;21:395–400. - PubMed
-
- Blozovski D, Cudennec A. Passive avoidance learning in the young rat. Developmental Psychobiology. 1980;13:513–518. - PubMed
-
- Brennan PA, Keverne EB. Neural mechanisms of mammalian olfactory learning. Progress in Neurobiology. 1997;51:457–481. - PubMed
-
- Camp LL, Rudy JW. Changes in the categorization of appetitive and aversive events during postnatal development of the rat. Developmental Psychobiology. 1988;21:25–42. - PubMed
-
- Cedarbaum JM, Aghajanian GK. Noradrenergic neurons of the locus coeruleus: Inhibition by epinephrine and activation by the alpha antagonist piperoxane. Brain Research. 1976;112:413–419. - PubMed

