gamma-Aminobutyric acid, acting through gamma -aminobutyric acid type A receptors, inhibits the biosynthesis of neurosteroids in the frog hypothalamus
- PMID: 11087816
- PMCID: PMC17677
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.240269897
gamma-Aminobutyric acid, acting through gamma -aminobutyric acid type A receptors, inhibits the biosynthesis of neurosteroids in the frog hypothalamus
Abstract
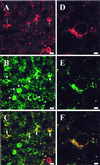
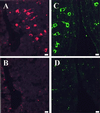
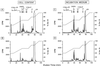
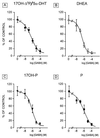
Most of the actions of neurosteroids on the central nervous system are mediated through allosteric modulation of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA(A)) receptor, but a direct effect of GABA on the regulation of neurosteroid biosynthesis has never been investigated. In the present report, we have attempted to determine whether 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3beta-HSD)-containing neurons, which secrete neurosteroids in the frog hypothalamus, also express the GABA(A) receptor, and we have investigated the effect of GABA on neurosteroid biosynthesis by frog hypothalamic explants. Double immunohistochemical labeling revealed that most 3beta-HSD-positive neurons also contain GABA(A) receptor alpha(3) and beta(2)/beta(3) subunit-like immunoreactivities. Pulse-chase experiments showed that GABA inhibited in a dose-dependent manner the conversion of tritiated pregnenolone into radioactive steroids, including 17-hydroxy-pregnenolone, progesterone, 17-hydroxy-progesterone, dehydroepiandrosterone, and dihydrotestosterone. The effect of GABA on neurosteroid biosynthesis was mimicked by the GABA(A) receptor agonist muscimol but was not affected by the GABA(B) receptor agonist baclofen. The selective GABA(A) receptor antagonists bicuculline and SR95531 reversed the inhibitory effect of GABA on neurosteroid formation. The present results indicate that steroid-producing neurons of the frog hypothalamus express the GABA(A) receptor alpha(3) and beta(2)/beta(3) subunits. Our data also demonstrate that GABA, acting on GABA(A) receptors at the hypothalamic level, inhibits the activity of several key steroidogenic enzymes, including 3beta-HSD and cytochrome P450(C17) (17alpha-hydroxylase).
Figures



Similar articles
-
The octadecaneuropeptide ODN stimulates neurosteroid biosynthesis through activation of central-type benzodiazepine receptors.J Neurochem. 2001 Jan;76(1):128-38. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00053.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11145985
-
The endozepine triakontatetraneuropeptide diazepam-binding inhibitor [17-50] stimulates neurosteroid biosynthesis in the frog hypothalamus.Neuroscience. 1998 Mar;83(2):555-70. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00362-x. Neuroscience. 1998. PMID: 9460762
-
Neuropeptide Y inhibits the biosynthesis of sulfated neurosteroids in the hypothalamus through activation of Y(1) receptors.Endocrinology. 2002 May;143(5):1950-63. doi: 10.1210/endo.143.5.8765. Endocrinology. 2002. PMID: 11956178
-
Steroid biosynthesis within the frog brain: a model of neuroendocrine regulation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Apr;1163:83-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03664.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19456330 Review.
-
Anatomical and biochemical evidence for the synthesis of unconjugated and sulfated neurosteroids in amphibians.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001 Nov;37(1-3):13-24. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(01)00110-2. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2001. PMID: 11744071 Review.
Cited by
-
Steroid modulation of GABAA receptor-mediated transmission in the hypothalamus: effects on reproductive function.Neuropharmacology. 2007 Jun;52(7):1439-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.01.022. Epub 2007 Feb 28. Neuropharmacology. 2007. PMID: 17433821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroactive Steroids and Affective Symptoms in Women Across the Weight Spectrum.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 May;43(6):1436-1444. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.269. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29090684 Free PMC article.
-
GABA receptor-mediated effects in the peripheral nervous system: A cross-interaction with neuroactive steroids.J Mol Neurosci. 2006;28(1):89-102. doi: 10.1385/jmn:28:1:89. J Mol Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16632878 Review.
-
GABA and neuroactive steroid interactions in glia: new roles for old players?Curr Neuropharmacol. 2007 Mar;5(1):47-64. doi: 10.2174/157015907780077132. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2007. PMID: 18615153 Free PMC article.
-
Vasotocin and mesotocin stimulate the biosynthesis of neurosteroids in the frog brain.J Neurosci. 2006 Jun 21;26(25):6749-60. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4469-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16793882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robel P, Baulieu E E. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1994;5:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Mensah-Nyagan A G, Do-Rego J L, Beaujean D, Luu-The V, Pelletier G, Vaudry H. Pharmacol Rev. 1999;51:63–82. - PubMed
-
- Jung-Testas I, Hu Z Y, Baulieu E E, Robel P. Endocrinology. 1989;125:2083–2091. - PubMed
-
- Weidenfield J, Sziegel R A, Chowers I. J Steroid Biochem. 1980;13:961–963. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

