Involvement of 5-HT(3) receptors in the nucleus accumbens in the potentiation of cocaine-induced behaviours in the rat
- PMID: 11090100
- PMCID: PMC1572452
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703687
Involvement of 5-HT(3) receptors in the nucleus accumbens in the potentiation of cocaine-induced behaviours in the rat
Abstract
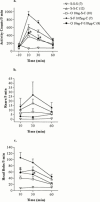
1. The present study investigated the central effects of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) fluoxetine and the role of 5-hydroxytryptamine(3) (5-HT(3)) receptors in the core of the nucleus accumbens (NAc) on cocaine-induced behavioural changes in rats. 2. The 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist ondansetron (1 or 10 ng) was microinjected bilaterally into the core of the NAc 60 min prior to peripheral cocaine (15 mg kg(-1), i.p.) administration followed by the assessment of locomotor activity, rearing activity and head bobs. Both doses of ondansetron attenuated cocaine's stimulatory effect on behaviours. 3. Fluoxetine (0.05 or 5 microg) microinjected bilaterally into the core of the NAc 30 min before peripheral administration of cocaine produced dose-dependent biphasic effects on cocaine-induced behaviours. Intra-NAc administration of 0.05 microg fluoxetine resulted in a potentiation of cocaine-induced behaviours, while the higher dose of the SSRI (5 microg) attenuated the stimulant effect of cocaine on behaviours. 4. To investigate a possible involvement of 5-HT(3) receptors in fluoxetine's facilitatory action, ondansetron (10 ng) was microinjected 30 min prior to fluoxetine (0.05 microg), which resulted in a significant attenuation of the facilitatory effect of fluoxetine on cocaine-induced behaviours. 5. Thus, 5-HT(3) receptors in the core of the NAc appear to mediate stimulatory effects on cocaine-induced locomotor activity, rears and head bobs, whereas the attenuation of cocaine-induced behaviours by fluoxetine at the higher dose, suggests the involvement of a different 5-HT receptor subtype.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Involvement of serotonin in the modulation of cocaine-induced locomotor activity in the rat.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1998 Mar;59(3):595-611. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(97)00473-5. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1998. PMID: 9512061
-
Modulation of cocaine-induced locomotor activity, rears and head bobs by application of WAY100635 into the dorsal and median raphe nuclei of the rat.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1999 Aug;360(2):129-34. doi: 10.1007/s002109900058. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10494881
-
Modulatory effect of p-chlorophenylalanine microinjected into the dorsal and median raphe nuclei on cocaine-induced behaviour in the rat.Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 Jun 25;374(3):329-40. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(99)00333-7. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10422777
-
Effects of serotonin (5-HT)(1B) receptor ligands, microinjected into accumbens subregions, on cocaine discrimination in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2002 Sep;366(3):226-34. doi: 10.1007/s00210-002-0583-5. Epub 2002 Jun 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12172705
-
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors enhance cocaine-induced locomotor activity and dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens.Neuropharmacology. 2003 Mar;44(3):342-53. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(02)00381-7. Neuropharmacology. 2003. PMID: 12604093
Cited by
-
Differences in regional cerebral blood flow response to a 5HT3 antagonist in early- and late-onset cocaine-dependent subjects.Addict Biol. 2014 Mar;19(2):250-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2012.00450.x. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Addict Biol. 2014. PMID: 22458709 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of 5-HT3 receptors leads to altered responses 6 months after MDMA treatment.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2010 Mar;117(3):285-92. doi: 10.1007/s00702-009-0357-z. Epub 2010 Jan 6. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2010. PMID: 20052506
-
The role of 5-HT3 receptors in drug abuse and as a target for pharmacotherapy.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008 Nov;7(5):454-67. doi: 10.2174/187152708786927886. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 19128203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patch Clamp Study of Serotonin-Gated Currents via 5-HT Type 3 Receptors by Using a Novel Approach SHAM for Receptor Channel Scanning.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2004;2004(1):10-15. doi: 10.1155/S1110724304302020. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15123883 Free PMC article.
-
The reinforcing effects of ethanol within the nucleus accumbens shell involve activation of local GABA and serotonin receptors.J Psychopharmacol. 2015 Jun;29(6):725-33. doi: 10.1177/0269881115581982. Epub 2015 Apr 28. J Psychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25922425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADELL A., ARTIGAS F. Differential effects of clomipramine given locally or systemically on extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in raphe nuclei and frontal cortex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1991;343:237–244. - PubMed
-
- ALHEID G.F., HEIMER L. New perspectives in basal forebrain organization of special relevance for neuropsychiatric disorders: The striatopallidal, amygdaloid, and corticopetal components of substantia innominata. Neuroscience. 1988;27:1–39. - PubMed
-
- BAGDY E., SOLYOM S., HARSING L.G. Feedback stimulation of somatodendritic serotonin release: A 5-HT3 receptor-mediated effect in the raphe nuclei of the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 1998;45:203–208. - PubMed
-
- BAUMANN P.A., WALDMEIER P.C. Further evidence for negative feedback control of serotonin release in the central nervous system. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1981;317:36–43. - PubMed
-
- BRADBERRY C.W., ROTH R.H. Cocaine increases extracellular dopamine in rat nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area as shown by in vivo microdialysis. Neurosci. Lett. 1989;103:97–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

