Inhibitory effects of JTV-519, a novel cardioprotective drug, on potassium currents and experimental atrial fibrillation in guinea-pig hearts
- PMID: 11090108
- PMCID: PMC1572470
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703713
Inhibitory effects of JTV-519, a novel cardioprotective drug, on potassium currents and experimental atrial fibrillation in guinea-pig hearts
Abstract
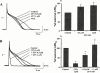
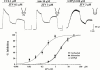
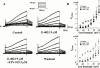
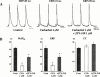
1. We investigated the effects of JTV-519 (4-[3-(4-benzylpiperidin-1-yl)propionyl]-7-methoxy-2,3,4, 5-tetrahydro-1,4-benzothiazepine monohydrochloride), a novel cardioprotective drug, on the repolarizing K(+) currents in guinea-pig atrial cells by use of patch-clamp techniques. We also evaluated the effects of JTV-519 on experimental atrial fibrillation (AF) in isolated guinea-pig hearts. 2. In atrial cells stimulated at 0.2 Hz, JTV-519 in concentrations of 0.3 and 1 microM slightly prolonged the action potential duration (APD). The drug also reversed the action potential shortening induced by the muscarinic agonist carbachol in a concentration-dependent manner. 3. The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-operated K(+) current (I(K.ACh)) was activated by the extracellular application of carbachol (1 microM), adenosine (10 microM) or by the intracellular loading of GTP gamma S (100 microM). JTV-519 inhibited the carbachol-, adenosine- and GTP gamma S-induced I(K.ACh) with the IC(50) values of 0.12, 2.29 and 2.42 microM, respectively, suggesting that the drug may inhibit I(K.ACh) mainly by blocking the muscarinic receptors. 4. JTV-519 (1 microM) inhibited the delayed rectifier K(+) current (I(K)). Electrophysiological analyses indicated that the drug preferentially inhibits I(Kr) (rapidly activating component) but not I(Ks) (slowly activating component). 5. In isolated hearts, perfusion of carbachol (1 microM) shortened monophasic action potential (MAP) and effective refractory period (ERP), and lowered atrial fibrillation threshold (AFT). Addition of JTV-519 (1 microM) inhibited the induction of AF by prolonging MAP and ERP. 6. We conclude that JTV-519 can exert antiarrhythmic effects against AF by inhibiting repolarizing K(+) currents. The drug may be useful for the treatment of AF in patients with ischaemic heart disease.
Figures
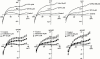

References
-
- ALLESSIE M.A.Reentrant mechanisms underlying atrial fibrillation Cardiac Electrophysiology: From Cell to Bedside 1995Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Company; 562–566.2nd edn. eds. Zipes, D.P. & Jalife, J., pp
-
- BALSER J.R., BENETT P.B., HONDEGHEM L.M., RODEN D.M. Suppression of time-dependent outward current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes: Action of quinidine and amiodarone. Circ. Res. 1991;69:519–529. - PubMed
-
- BEHAR S., ZAHAVI Z., GOLDBOURT U., REICHER-REISS H., for the SPRINT Study Group Long-term prognosis of patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation complicating acute myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 1992;13:45–50. - PubMed
-
- FABIATO A., FABIATO F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J. Physiol (Paris). 1979;75:463–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

