In vitro reconstitution of a functional duck hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase: posttranslational activation by Hsp90
- PMID: 11090140
- PMCID: PMC112423
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.24.11447-11455.2000
In vitro reconstitution of a functional duck hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase: posttranslational activation by Hsp90
Abstract
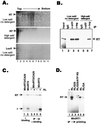
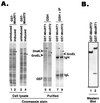
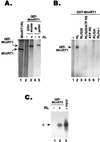
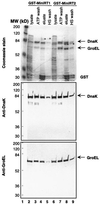
Reverse transcription in hepatitis B viruses is initiated through a unique protein priming mechanism whereby the viral reverse transcriptase (RT) first assembles into a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex with its RNA template and then initiates DNA synthesis de novo using the RT itself as a protein primer. RNP formation and protein priming require the assistance of host cell factors, including the molecular chaperone heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90). To better understand the mechanism of RT activation by Hsp90, we have now mapped the minimal RT sequences of the duck hepatitis B virus that are required for chaperone binding, RNP formation, and protein priming. Furthermore, we have reconstituted in vitro both RNP formation and protein priming using purified RT proteins and host factors. Our results show that (i) Hsp90 recognizes two independent domains of the RT, both of which are necessary for RNP formation and protein priming; (ii) Hsp90 function is required not only to establish, but also to maintain, the RT in a state competent for RNA binding; and (iii) Hsp90 is not required during RT synthesis and can activate the RT posttranslationally. Based on these findings, we propose a model for Hsp90 function whereby the chaperone acts as an active interdomain bridge to bring the two RT domains into a poised but labile conformation competent for RNP formation. It is anticipated that the reconstitution system established here will facilitate the isolation of additional host factors required for RT functions and further elucidation of the mechanisms of RT activation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Heat shock protein 90-independent activation of truncated hepadnavirus reverse transcriptase.J Virol. 2003 Apr;77(8):4471-80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.8.4471-4480.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12663754 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperone activation of the hepadnaviral reverse transcriptase for template RNA binding is established by the Hsp70 and stimulated by the Hsp90 system.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(18):6124-36. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm628. Epub 2007 Sep 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17804463 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro reconstitution of functional hepadnavirus reverse transcriptase with cellular chaperone proteins.J Virol. 2002 Jan;76(1):269-79. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.1.269-279.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11739692 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Hsp90-independent in vitro activation by Hsc70 and Hsp40 of duck hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase, an assumed Hsp90 client protein.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 19;278(38):36128-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301069200. Epub 2003 Jul 8. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12851401
-
Hepatitis B viruses: reverse transcription a different way.Virus Res. 2008 Jun;134(1-2):235-49. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.12.024. Epub 2008 Mar 12. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 18339439 Review.
Cited by
-
Noncompetitive inhibition of hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase protein priming and DNA synthesis by the nucleoside analog clevudine.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Sep;57(9):4181-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00599-13. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23774432 Free PMC article.
-
Stress proteins: the biological functions in virus infection, present and challenges for target-based antiviral drug development.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jul 13;5(1):125. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00233-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32661235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase requires the mammalian chaperone hsp90 for proper localization to the nucleus.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(16):10740-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10740-10749.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16051866 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Sin Nombre virus infection in the deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) model: sites of replication and strand-specific expression.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(2):1540-50. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.2.1540-1550.2002. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12502867 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of the host DNA-repair enzyme TDP2 in formation of the covalently closed circular DNA persistence reservoir of hepatitis B viruses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Oct 7;111(40):E4244-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1409986111. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25201958 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beasley R P, Lin C C, Hwang L Y, Chien C S. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. Lancet. 1981;ii:1129–1133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

