The inhibition of cutaneous T cell apoptosis may prevent resolution of inflammation in atopic eczema
- PMID: 11091268
- PMCID: PMC1905772
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01333.x
The inhibition of cutaneous T cell apoptosis may prevent resolution of inflammation in atopic eczema
Abstract
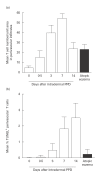
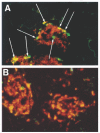
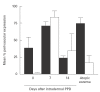
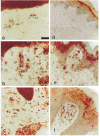
Atopic eczema (AE) is characterized by the persistence of infiltrating T lymphocytes in the dermis. To test the hypothesis that dysregulation of normal T cell apoptosis may contribute to the pathogenesis and chronicity of AE we compared patients with a normal resolving immune response (Mantoux reaction (MR)) induced in healthy volunteers by cutaneous PPD injection. Significantly less T cell apoptosis was observed in lesional skin of AE patients compared with either the peak or the resolution phase of the MR (P < 0.0001). The low incidence of T cell apoptosis in AE was associated with significantly increased levels of Bcl-2 relative to Bax (P < 0.0001) and significantly decreased CD95-L expression (P < 0.002) compared with the resolving MR. The cytokines IL-15 and interferon-beta (IFN-beta), which prevent activated T cell apoptosis, were expressed maximally on day 7 and day 14 of the MR, respectively. In contrast, AE patients expressed high levels of both IL-15 and IFN-beta in cutaneous lesions at the same time. This suggests that the co-expression of two anti-apoptotic cytokines, which are not found together during resolving cutaneous responses, may contribute to excessive T cell survival which leads to the persistence of inflammation in patients with AE.
Figures
References
-
- Krammer PH, Behrmann I, Daniel P, Dhein J, Debatin KM. Regulation of apoptosis in the immune system. Curr Opin Immunol. 1994;6:279–89. - PubMed
-
- Akbar AN, Salmon M. Cellular environments and apoptosis: tissue microenvironments control activated T cell death. Immunol Today. 1997;18:72–76. - PubMed
-
- Pilling D, Akbar AN, Girdlestone J, et al. Interferon-beta mediates stromal cell rescue of T cells from apoptosis. Eur J Immunol. 1999;29:1041–50. - PubMed
-
- Salmon M, Pilling D, Borthwick NJ, Akbar AN. Inhibition of T cell apoptosis: a mechanism for the persistence of chronic inflammation. Immunologist. 1997;5:87–92.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

