High-frequency flp recombinase-mediated inversions of the oriC-containing region of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa genome
- PMID: 11092871
- PMCID: PMC94836
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.24.7070-7074.2000
High-frequency flp recombinase-mediated inversions of the oriC-containing region of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa genome
Abstract
The genomes of the two clonally derived Pseudomonas aeruginosa prototypic strains PAO1 and DSM-1707 differ by the presence of a 2. 19-Mb inversion including oriC. Integration of two Flp recombinase target sites near the rrn operons containing the inversion endpoints in PAO1 led to Flp-catalyzed inversion of the intervening 1.59-Mb fragment, including oriC, at high frequencies (83%), favoring the chromosome configuration found in DSM-1707. The results indicate that the oriC-containing region of the P. aeruginosa chromosome can readily undergo and tolerate large inversions.
Figures
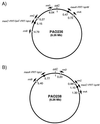



References
-
- Anagnostopoulos C. Genetic rearrangements in Bacillus subtilis. In: Drlica K, Riley M, editors. The bacterial chromosome. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology; 1990. pp. 361–371.
-
- Hoang T T, Karkhoff-Schweizer R R, Kutchma A J, Schweizer H P. A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: application for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene. 1998;212:77–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

