Neurally mediated syncope
Abstract
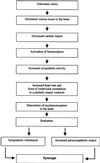
Neurally mediated syncope is a disorder of the autonomic regulation of postural tone, which results in hypotension, bradycardia, and loss of consciousness. A wide variety of stimuli can trigger this reflex, the most common stimulus being orthostatic stress. Typically, a patient with neurally mediated syncope experiences nausea, lightheadedness, a feeling of warmth, and pallor before abruptly losing consciousness. If the cause of syncope is unclear, a stepwise approach is necessary to arrive at the diagnosis. The diagnosis of neurally mediated syncope can be confirmed by a head-up tilt-table test. Treatment options include behavioral modification and several pharmacologic therapies. For severe recurrent syncope unresponsive to conventional treatment, a pacemaker can be implanted.
Figures
References
-
- Mark AL. The Bezold-Jarisch reflex revisited: clinical implications of inhibitory reflexes originating in the heart. J Am Coll Cardiol 1983;1:90–102. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen TN, Morgan BJ, Scherrer U, Vissing SF, Lange RA, Johnson N, et al. Relative contributions of cardiopulmonary and sinoaortic baroreflexes in causing sympathetic activation in the human skeletal muscle circulation during orthostatic stress. Circ Res 1993;73:367–78. - PubMed
-
- Grubb BP, Karas B. Clinical disorders of the autonomic nervous system associated with orthostatic intolerance: an overview of classification, clinical evaluation, and management. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 1999;22:798–810. - PubMed
-
- Morillo CA, Ellenbogen KA, Fernando Pava L. Pathophysiologic basis for vasodepressor syncope. Cardiol Clinic 1997; 15:233–49. - PubMed
-
- Fitzpatrick AP, Banner N, Cheng A, Yacoub M, Sutton R. Vasovagal reactions may occur after orthotopic heart transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993;21:1132–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources