Vav3 mediates receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling, regulates GTPase activity, modulates cell morphology, and induces cell transformation
- PMID: 11094073
- PMCID: PMC102179
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.24.9212-9224.2000
Vav3 mediates receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling, regulates GTPase activity, modulates cell morphology, and induces cell transformation
Abstract
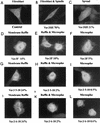
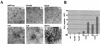
A recently reported new member of the Vav family proteins, Vav3 has been identified as a Ros receptor protein tyrosine kinase (RPTK) interacting protein by yeast two-hybrid screening. Northern analysis shows that Vav3 has a broad tissue expression profile that is distinct from those of Vav and Vav2. Two species of Vav3 transcripts, 3.4 and 5.4 kb, were detected with a differential expression pattern in various tissues. Transient expression of Vav in 293T and NIH 3T3 cells demonstrated that ligand stimulation of several RPTKs (epidermal growth factor receptor [EGFR], Ros, insulin receptor [IR], and insulin-like growth factor I receptor [IGFR]) led to tyrosine phosphorylation of Vav3 and its association with the receptors as well as their downstream signaling molecules, including Shc, Grb2, phospholipase C (PLC-gamma), and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase. In vitro binding assays using glutathione S-transferase-fusion polypeptides containing the GTPase-binding domains of Rok-alpha, Pak, or Ack revealed that overexpression of Vav3 in NIH 3T3 cells resulted in the activation of Rac-1 and Cdc42 whereas a deletion mutant lacking the N-terminal calponin homology and acidic region domains activated RhoA and Rac-1 but lost the ability to activate Cdc42. Vav3 induced marked membrane ruffles and microspikes in NIH 3T3 cells, while the N-terminal truncation mutants of Vav3 significantly enhanced membrane ruffle formation but had a reduced ability to induce microspikes. Activation of IR further enhanced the ability of Vav3 to induce membrane ruffles, but IGFR activation specifically promoted Vav3-mediated microspike formation. N-terminal truncation of Vav3 activated its transforming potential, as measured by focus-formation assays. We conclude that Vav3 mediates RPTK signaling and regulates GTPase activity, its native and mutant forms are able to modulate cell morphology, and it has the potential to induce cell transformation.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Distinct role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Rho family GTPases in Vav3-induced cell transformation, cell motility, and morphological changes.J Biol Chem. 2002 May 17;277(20):17638-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111575200. Epub 2002 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11884391
-
Signaling complexes and protein-protein interactions involved in the activation of the Ras and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathways by the c-Ret receptor tyrosine kinase.J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 15;275(50):39159-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006908200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10995764
-
Ret oncogene signal transduction via a IRS-2/PI 3-kinase/PKB and a SHC/Grb-2 dependent pathway: possible implication for transforming activity in NIH3T3 cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000 Sep 25;167(1-2):69-76. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(00)00283-5. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 11000521
-
CSF-1 signal transduction.J Leukoc Biol. 1997 Aug;62(2):145-55. doi: 10.1002/jlb.62.2.145. J Leukoc Biol. 1997. PMID: 9261328 Review.
-
Vav family exchange factors: an integrated regulatory and functional view.Small GTPases. 2014;5(2):9. doi: 10.4161/21541248.2014.973757. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25483299 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cell growth and metastasis in pancreatic cancer: is Vav the Rho'd to activation?Int J Gastrointest Cancer. 2002;31(1-3):5-13. doi: 10.1385/IJGC:31:1-3:5. Int J Gastrointest Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12622410 Review.
-
Critical but distinct roles for the pleckstrin homology and cysteine-rich domains as positive modulators of Vav2 signaling and transformation.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;22(8):2487-97. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.8.2487-2497.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11909943 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity Analysis of the NPM-ALK Signalling Network Reveals Important Pathways for Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Combination Therapy.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 26;11(9):e0163011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163011. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27669408 Free PMC article.
-
Vav2 is required for cell spreading.J Cell Biol. 2001 Jul 9;154(1):177-86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200103134. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11448999 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Regulation of the Small Rho GTPase Regulators-Complexities and Opportunities in Targeting Cancer Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 28;12(5):1092. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051092. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32353968 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abe K, Rossman K L, Liu B, Ritola K D, Chiang D, Campbell S L, Burridge K, Der C J. Vav2 is an activator of Cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:10141–10149. - PubMed
-
- Bartel P L, Chien C T, Sternglanz R, Fields S. Using the two-hybrid system to detect protein-protein interactions. In: Hartley D A, editor. Cellular interactions in development: a practical approach. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press; 1993. pp. 153–179.
-
- Bertagnolo V, Marchisio M, Volinia S, Caramelli E, Capitani S. Nuclear association of tyrosine-phosphorylated Vav to phospholipase C-γ 1 and phosphoinositide 3-kinase during granulocytic differentiation of HL-60 cells. FEBS Lett. 1998;441:480–484. - PubMed
-
- Bubeck Wardenburg J, Pappu R, Bu J Y, Mayer B, Chernoff J, Straus D, Chan A C. Regulation of PAK activation and the T cell cytoskeleton by the linker protein SLP-76. Immunity. 1998;9:607–616. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
