Nutrition in the intensive care unit
- PMID: 11094484
- PMCID: PMC137235
- DOI: 10.1186/cc360
Nutrition in the intensive care unit
Abstract
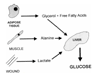
Nutritional support has become a routine part of the care of the critically ill patient. It is an adjunctive therapy, the main goal of which is to attenuate the development of malnutrition, yet the effectiveness of nutritional support is often thwarted by an underlying hostile metabolic milieu. This requires that these metabolic changes be taken into consideration when designing nutritional regimens for such patients. There is also a need to conduct large, multi-center studies to acquire more knowledge of the cost-benefit and cost effectiveness of nutritional support in the critically ill.
Figures
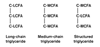
References
-
- Wolfe RR. Herman Award Lecture 1996: relation of metabolic studies to clinical nutrition: the example of burn injury. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996;64:800–808. - PubMed
-
- Thorell A, Nygren J, Hirshman MF, et al. Surgery-induced insulin resistance in human patients: relation to glucose transport and utilization. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:E754–E761. - PubMed
-
- Green CJ, Campbell IT, O'Sullivan E, et al. Septic patients in multiple organ failure can oxidize infused glucose, but non-oxidative disposal (storage) is impaired. Clin Sci (Colch) 1995;89:601–609. - PubMed
-
- Chiolero R, Revelly JP, Tappy L. Energy metabolism in sepsis and injury. Nutrition. 1997;13 (suppl 9):45S–51S. - PubMed
-
- Strommer L, Permert J, Arnelo U, et al. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance after trauma: insulin signaling and glucose transport. . Am J Physiol. 1998;275:E351–E358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

